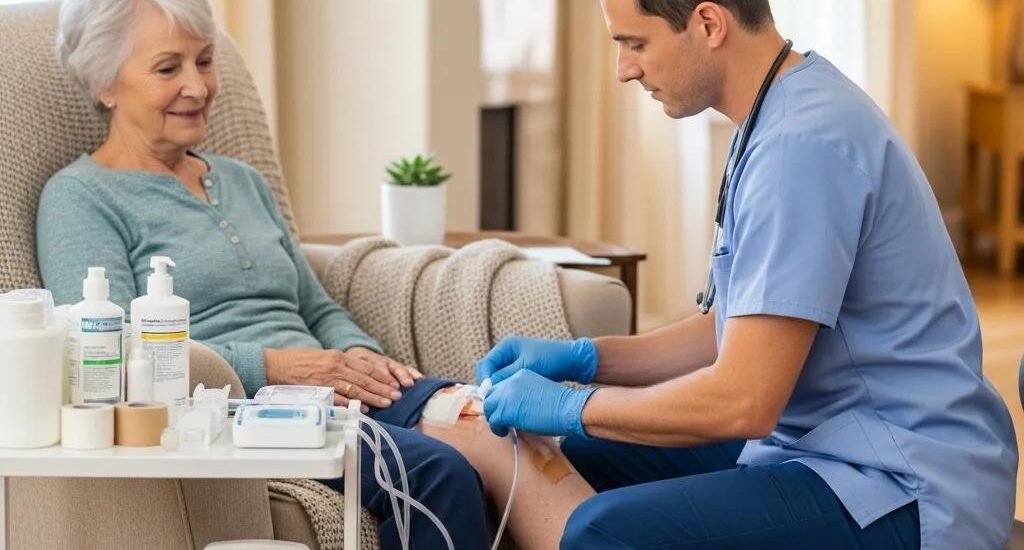
Advanced Wound Care Technology: Regenerative Healing and Modern Treatments
Wound care has progressed rapidly, unlocking tools that speed recovery and improve outcomes for people with chronic or complex wounds. This article outlines today’s most promising advances—regenerative therapies, mobile care models, and evidence-based treatments—so patients and clinicians can understand how these approaches work, who benefits, and what to expect during care. Many healing challenges stem from limited mobility, underlying health conditions, or wound complexity; modern wound-care technology addresses these barriers with precise, patient-centered solutions. Read on for an overview of mobile wound services, regenerative options, negative pressure therapy, and typical care pathways.
Recent studies and reviews reinforce that wound care is evolving across both established and emerging approaches.
Innovative Technologies for Advanced Wound Healing & Management
This review compares traditional surgical and non-surgical wound treatments with newer topical and scaffold-based approaches. It highlights how techniques such as debridement, flaps, and grafts remain important while modern dressings, hydrogels, nanoparticles, growth factors, and bioactive materials are expanding options for cutaneous wound repair. The paper also discusses bioengineered skin substitutes and scaffold-based strategies that support advanced healing.
Current trends on innovative technologies in topical wound care for advanced healing and management, Q Saifullah, 2024
What is Advanced Mobile Wound Care and How Does It Improve Healing?
Advanced mobile wound care brings specialized wound assessment and treatment to the patient’s home or another convenient location. Delivering care where the patient lives removes travel barriers, allows more frequent monitoring, and supports tailored interventions—factors that together improve adherence and speed recovery. Mobile teams combine clinical expertise with portable technologies to provide safe, timely, and personalized wound management outside the clinic.
How Does Mobile Wound Care Overcome Mobility Barriers?
By delivering skilled care at home, mobile wound services remove the need for frequent clinic visits—especially important for older adults or people with limited transportation. Regular, in‑home visits let clinicians adjust treatments quickly, spot complications earlier, and teach caregivers practical steps for daily wound care. That consistency often translates into fewer setbacks and better overall healing.
What Are the Benefits of Personalized Treatment Plans in Mobile Wound Care?
Personalized plans are built around the wound type, medical history, and the patient’s daily routine. Customizing dressings, offloading strategies, and adjunctive therapies—sometimes including regenerative products—helps target the factors slowing healing. For example, a person with a diabetic foot ulcer may receive a combination of specialty dressings, pressure relief, and targeted therapies that together support faster, safer recovery.
Cutting-Edge Wound Care: Regenerative & Modern Treatments
Regenerative wound care leverages therapies—like stem cells and biologic products—that support the body’s own repair mechanisms. Stem cell approaches aim to reduce inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration, while biologics (products derived from living tissues) deliver growth factors and structural scaffolds that encourage new tissue formation. Used appropriately, these options can shorten recovery and improve the quality of healed tissue in chronic wounds.
What Role Do Stem Cells Play in Healing Chronic Wounds?
Stem cells can help restore the cellular environment needed for healing: they reduce harmful inflammation, encourage the formation of new blood vessels, and differentiate into cell types that repair tissue. Evidence shows stem-cell–based therapies may increase healing rates in wounds that have not responded to standard care, offering a valuable option when conventional methods fall short.
The role of stem cells is increasingly incorporated into engineered tissues and grafts for chronic wound management.
Stem Cell Therapy & Bioengineered Tissues for Chronic Wound Care
This work outlines how bioengineered tissues loaded with stem cells form the foundation of a growing therapeutic strategy for chronic wounds, supporting regeneration and improved repair.
Stem cell therapy in wound healing, I Benedek, 2017
How Do Biologic Wound Dressings and Amniotic Tissue Patches Support Regeneration?
Biologic dressings and amniotic membrane patches create a healing environment rich in growth factors and structural cues. They act as scaffolds for healthy cell migration, reduce inflammation, and supply bioactive molecules that guide tissue repair. For many chronic wounds, these products help jump‑start stalled healing by combining physical protection with biologic support.
Clinical evidence supports the use of amniotic membranes and other biologic materials to improve multiple aspects of wound healing.
Amniotic Membrane for Wound Healing & Tissue Regeneration
Amniotic membrane transplantation (AMT) has become a versatile tool in wound care and tissue regeneration. Reviews show AMT can reduce pain, lower infection risk, and support epithelialization—acting through angiogenesis and immune modulation to aid both acute and chronic wound healing.
Amniotic Membrane Transplantation for Wound Healing,
Tissue Regeneration and Immune Modulation, UPS Parmar, 2025
What Are the Benefits and Applications of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy?
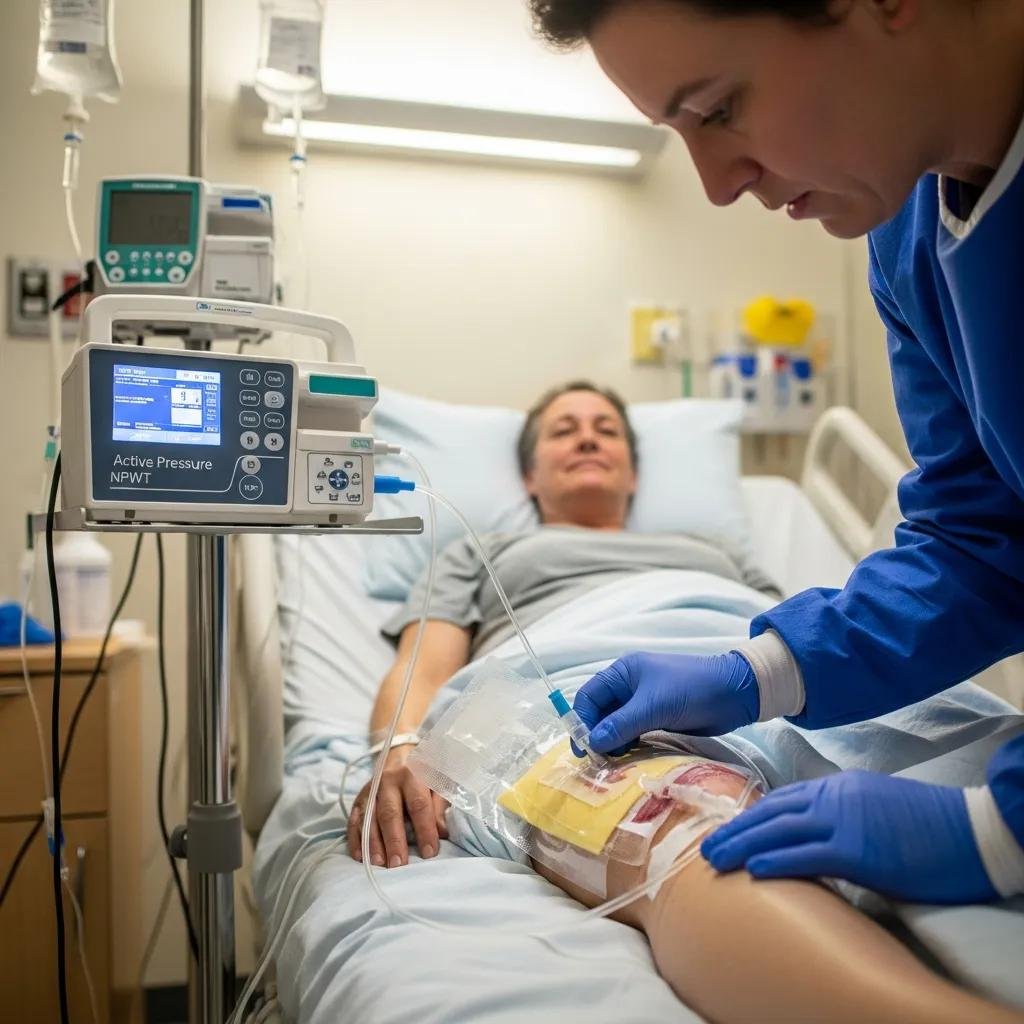
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses controlled suction to remove fluid, reduce swelling, and encourage the formation of healthy granulation tissue. Widely adopted for complex or slow‑healing wounds, NPWT creates an environment that supports tissue repair while lowering complication risks.
How Does NPWT Accelerate Healing Timelines?
NPWT promotes granulation and draws out excess exudate, which helps reduce edema and bacterial burden. By improving local blood flow and providing a stable wound environment, NPWT often shortens the time to closure compared with standard dressings—especially in deep or non‑healing wounds.
Which Chronic Wounds Benefit Most from NPWT?
NPWT is commonly used for diabetic foot ulcers, pressure injuries, post‑surgical wounds, and other chronic wounds that resist conventional care. Its ability to manage drainage, support tissue growth, and help control infection makes it a strong option for wounds requiring active, ongoing management.
Which Advanced Wound Treatment Options Are Available for Common Chronic Wounds?
A range of advanced treatments exists to address the most frequent chronic wounds. These options combine established modalities with newer regenerative products to improve healing rates and reduce complications. Choosing the right combination depends on wound type, patient health, and treatment goals.
How Are Diabetic Foot Ulcers Treated with Latest Innovations?
Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers often blends specialty dressings, NPWT, offloading strategies, and regenerative therapies when appropriate. Biologic dressings that deliver growth factors and scaffold support can enhance tissue repair, while NPWT helps control fluid and promote healthy tissue formation—together reducing infection risk and supporting recovery.
What Regenerative Approaches Address Venous Leg and Pressure Ulcers?
Venous leg ulcers and pressure injuries may respond to stem‑cell therapies, amniotic or other biologic dressings, and supportive measures that improve circulation and relieve pressure. These regenerative approaches aim to restore the wound environment, reduce inflammation, and provide the structural support needed for new tissue to form.
What Should Patients Expect During Their Advanced Mobile Wound Care Journey?
Patients engaged in advanced mobile wound care should expect individualized treatment plans, regular assessments, and close communication with their care team. The process emphasizes clear goals, practical education for self‑care, and adjustments as the wound responds to therapy—so progress is monitored and complications are addressed promptly.
How Is Pain and Infection Managed in Advanced Wound Care?
Pain and infection are managed proactively using appropriate analgesics, antimicrobial dressings, topical or systemic antibiotics when indicated, and careful wound hygiene. Mobile teams evaluate pain at each visit and tailor interventions to keep patients comfortable while minimizing infection risk.
What Are Typical Healing Timelines and Follow-Up Procedures?
Healing timelines vary by wound type, size, and individual health. Expect scheduled follow-ups to track progress, change dressings, and adjust therapies. These routine visits are essential to confirm healing, detect setbacks early, and adapt the plan until the wound is stable.
How Does Healix360 Integrate Latest Innovations into Mobile Wound Care Services?
Healix360’s Advanced Mobile Wound Care team combines evidence‑based practices with regenerative options to deliver comprehensive care where patients live. Serving communities including Glendale, CA, our clinicians use proven technologies and personalized plans to close wounds faster and reduce complications.
What Makes Healix360’s Regenerative Medicine Expertise Stand Out?
Healix360’s experience in regenerative medicine rests on a focus on outcomes and training in current therapeutic techniques. Our specialists evaluate each case to recommend the most effective, evidence‑based modalities—helping patients achieve better healing and greater satisfaction with their care.
How Does Medicare Part B Coverage Facilitate Access to Advanced Treatments?
Medicare Part B helps make advanced wound-care services more accessible by covering a range of outpatient and home-based treatments, including many mobile wound visits and eligible therapies. This coverage reduces financial hurdles so more patients can receive timely, effective care.
| Treatment Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Wound Care | In‑home wound assessment and treatment | Easier access, greater comfort, consistent follow-up |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Biologic therapy using stem cells to support repair | Encourages tissue regeneration and reduces inflammation |
| Negative Pressure Therapy | Controlled suction to manage exudate and promote healing | Speeds granulation and can shorten healing time |
Combining these advanced options with individualized care highlights the value of tailoring treatment to the patient—ensuring each person receives the therapies most likely to work for their wound.
The field of wound care continues to advance, offering practical tools that improve healing and quality of life. By understanding mobile care models, regenerative therapies, and NPWT, patients and clinicians can make informed choices and work together toward better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences between traditional and advanced wound care treatments?
Traditional wound care relies on established methods like dressings, debridement, and surgical repair. Advanced care adds targeted technologies—such as negative pressure systems, biologic dressings, and regenerative therapies—that actively support tissue repair, manage wound biology, and address barriers to healing. The goal of advanced approaches is to improve healing speed and reduce complications in complex cases.
How can patients prepare for their first mobile wound care appointment?
Gather your medical history, a list of current medications, and details of prior wound treatments. Have the wound area accessible and clear a small workspace for the clinician. Write down questions or concerns so you can discuss priorities and expectations during the visit. These steps make the assessment smoother and more productive.
What types of chronic wounds are most commonly treated with regenerative therapies?
Regenerative therapies are often used for diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries—wounds that may resist standard treatments due to poor circulation, neuropathy, or persistent inflammation. Regenerative options aim to restore a healthier wound environment and stimulate tissue repair in these challenging cases.
What should patients know about the potential side effects of advanced wound care treatments?
Advanced treatments are generally safe, but side effects vary by therapy. For example, stem-cell procedures may cause temporary discomfort at application sites, while biologic products carry a small risk of allergic response. Your care team will review potential risks, monitor for reactions, and recommend steps to manage side effects if they occur.
How does the integration of technology improve patient outcomes in wound care?
Technology—like telehealth, digital imaging, and data analytics—supports faster, more accurate assessments and helps clinicians tailor treatments. Remote follow-up and objective tracking of wound progress let teams intervene sooner, refine care plans, and reduce unnecessary clinic visits, all of which contribute to better healing and patient experience.
What role does patient education play in successful wound care management?
Education empowers patients to follow treatment plans, spot signs of infection early, and perform daily care tasks correctly. Clear instructions about dressing changes, pressure relief, nutrition, and activity help patients participate actively in healing. Engaged, informed patients typically see better outcomes.
Conclusion
Modern wound-care technology—delivered through mobile services, biologic and regenerative options, and therapies like NPWT—offers meaningful advantages for people living with chronic wounds. When combined with personalized planning and close follow-up, these innovations can accelerate healing, reduce complications, and improve quality of life. Speak with your care team or contact Healix360 to learn which advanced solutions may be appropriate for your situation.