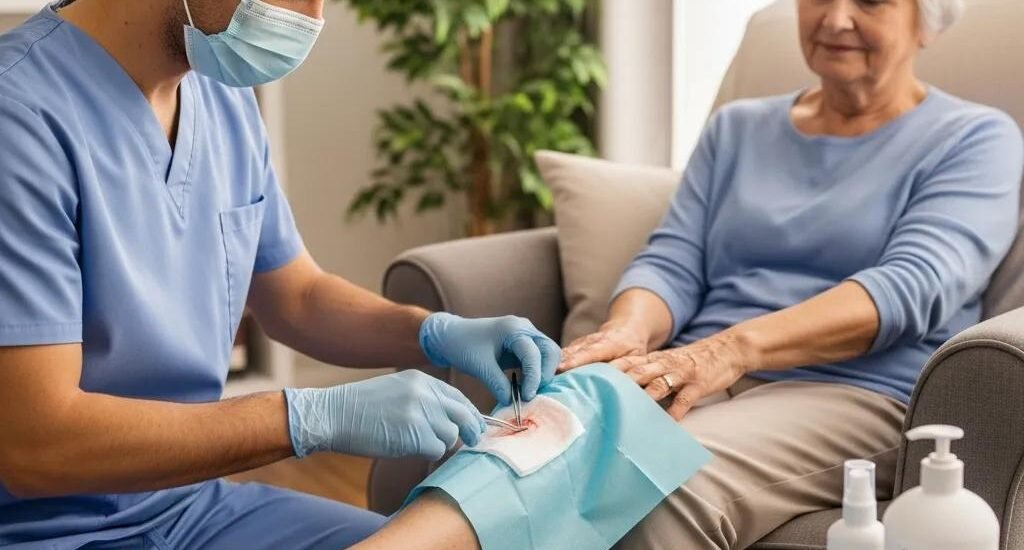
How Mobile Regenerative Wound Care Accelerates Healing at Home
Advanced wound care is changing outcomes for people living with long‑standing wounds. Modern regenerative therapies and targeted treatments can shorten recovery, lower complications, and restore daily life for patients who previously had few good options. Below we explain the common advanced approaches, how they work, and why mobile delivery — care in the patient’s home — often improves comfort, adherence, and results. With clear information about the healing process and available therapies, patients and families can make confident decisions about care.
What are advanced wound treatments, and how do they support healing?
Advanced wound treatments are clinically driven interventions that go beyond standard dressings: they use biologics, device‑based therapies, and targeted clinical assessment to correct underlying barriers to healing. By tackling infection, poor blood flow, persistent inflammation, and tissue loss, these approaches help the body complete the normal repair sequence and reach reliable closure.
Which regenerative therapies help wounds recover faster?
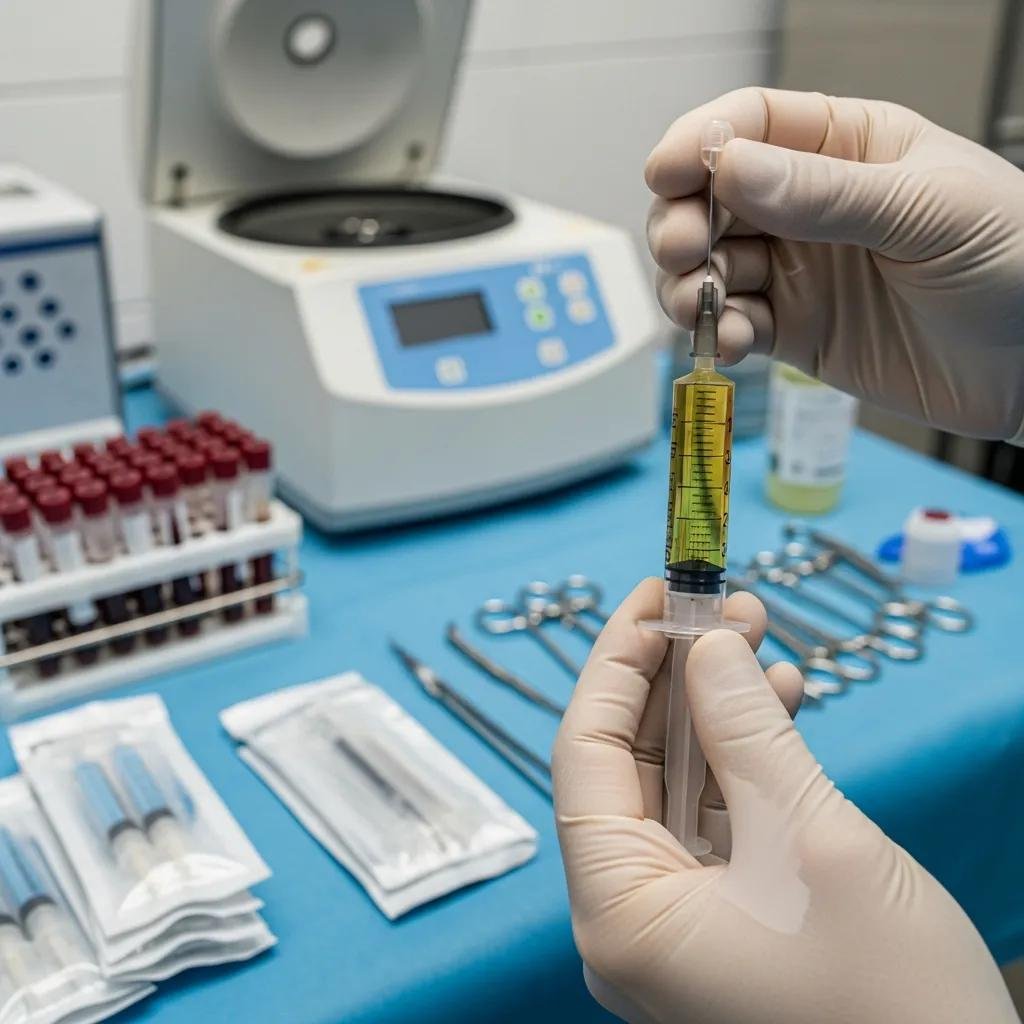
Regenerative wound therapies stimulate the body’s own repair systems. They include biologic products that deliver growth factors, cell‑based treatments that encourage tissue replacement, and engineered skin substitutes that provide a scaffold for new tissue. Platelet‑rich plasma (PRP), for example, concentrates a patient’s own platelets and growth factors to jump‑start repair. Other options — from skin grafts to tissue‑engineered matrices — supply healthy tissue or the signals needed for regeneration.
Clinical research continues to show promise for selected cellular therapies in helping stubborn wounds rebuild healthy tissue.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Advanced Chronic Wound Healing
Why it matters: hard‑to‑heal wounds need new biological strategies. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are appealing because they can differentiate into repair cells, modulate inflammation, and release growth factors and cytokines that promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Mesenchymal stem cells in chronic wounds: the spectrum from basic to advanced therapy, M Otero-Viñas, 2016
How do debridement and biologic dressings encourage tissue regrowth?
Debridement removes dead, infected, or non‑viable tissue so the wound bed is clean and able to respond to therapy. A well‑prepared wound bed improves the effect of topical agents, grafts, and biologic products and speeds healthy tissue formation.
Biologic dressings are designed to act like skin: they maintain a moist, protected environment and often include bioactive components that support cell migration and new tissue formation. Together with debridement, these dressings lower infection risk and create conditions favorable to regeneration.
How does mobile wound care make chronic wound treatment more accessible?
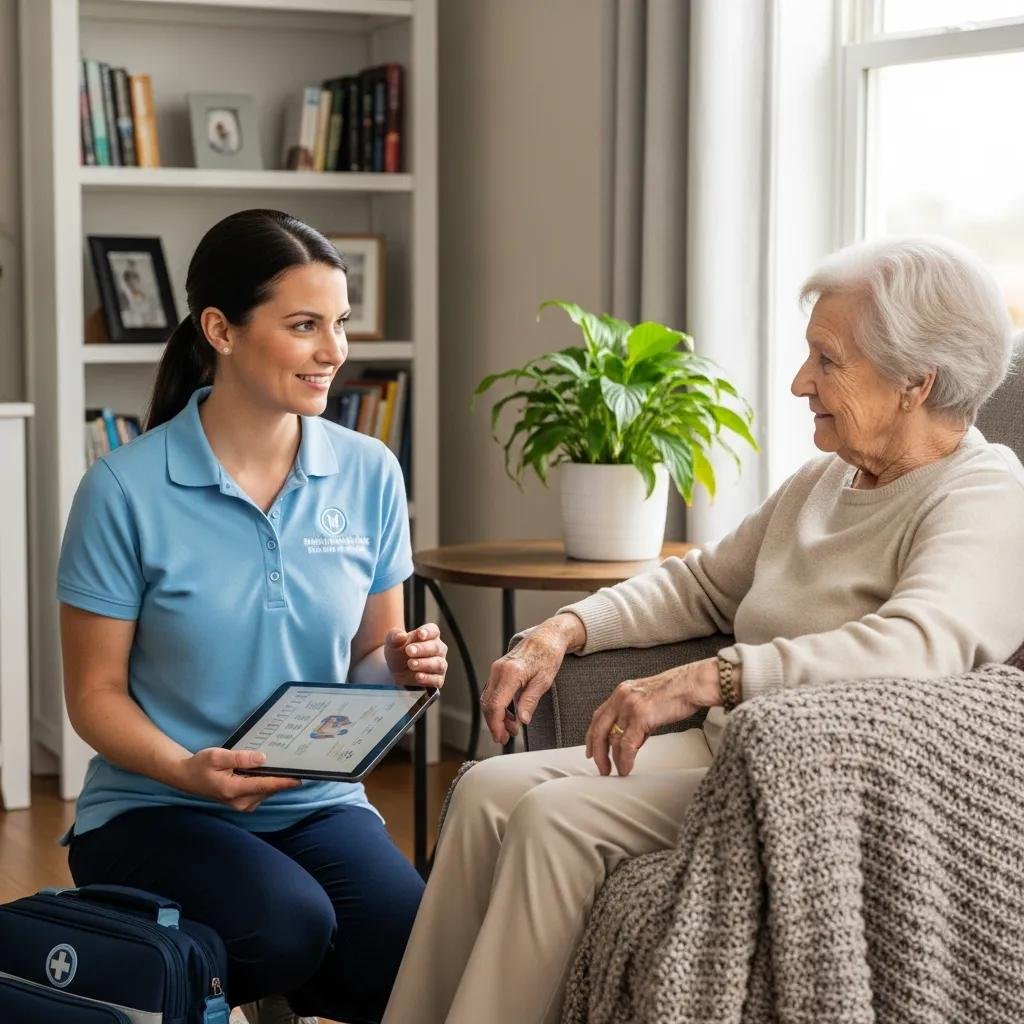

Mobile wound care brings advanced therapy to the patient’s home — reducing travel, lowering exposure to hospital infections, and improving comfort and continuity of care. Home visits allow clinicians to assess wounds in context, adjust treatments more frequently, and support patients and caregivers with practical education.
Telemedicine and secure data sharing further extend specialist access, enabling remote consultation and timely follow‑up between visits.
Mobile Wound Care Centers & Telemedicine
Model summary: mobile wound‑healing centers pair local clinicians with remote specialists using data transmission and store‑and‑forward systems over cellular and Wi‑Fi networks, allowing expert input and ongoing follow‑up without forcing the patient into a clinic.
The role of telemedicine in wound care: a review and analysis of a database of 5,795 patients from a mobile wound-healing center in Languedoc-Roussillon,
France, A Sood, 2016
What are the benefits of receiving wound care at home?
Home‑based wound care improves patient comfort and reduces disruptions to daily life. It lowers the chance of hospital‑acquired infections, supports emotional well‑being by treating patients in familiar surroundings, and enables more frequent monitoring so clinicians can adapt plans quickly as healing progresses.
How do mobile specialists create personalized treatment plans?
Mobile wound specialists perform thorough, on‑site assessments that account for the wound, the patient’s medical history, mobility and home environment. From that assessment they build a tailored plan — combining debridement, dressings, regenerative therapies, pressure‑relief strategies, and follow‑up — focused on practical steps that drive healing.
How does the wound healing process work for chronic wounds?
Knowing the stages of healing helps patients and clinicians target treatments. Chronic wounds often stall across the normal phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. Advanced care removes barriers at each stage so the repair sequence can continue to completion.
Which healing stages do advanced therapies improve?
Advanced therapies commonly target the inflammatory and proliferative phases: they reduce harmful inflammation, control infection, and provide signals or tissue that encourage new blood vessel growth and collagen formation. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), for example, improves perfusion and granulation tissue formation, which supports faster closure.
How do infection control and vascular assessment change outcomes?
Controlling infection is essential: regular wound checks, appropriate antimicrobials, and antimicrobial dressings prevent setbacks. Vascular assessment identifies circulation problems that can block healing; addressing vascular issues — medically or surgically when needed — lets advanced wound therapies work as intended and improves long‑term outcomes.
Which chronic wounds benefit most from mobile advanced treatments?
Mobile advanced treatments are especially helpful for diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries — wounds that commonly need multifaceted care and frequent monitoring to heal successfully.
How are diabetic foot and venous leg ulcers treated with regenerative approaches?
Diabetic foot ulcers typically need pressure off‑loading, infection control, and targeted dressings. Regenerative options such as skin substitutes, growth factor therapies, and PRP can stimulate tissue repair when used alongside pressure management and infection control. Venous leg ulcers respond well when compression therapy is combined with advanced dressings or biologics to improve local circulation and support regeneration.
In particular, PRP has been studied as a practical regenerative option for challenging diabetic foot ulcers with encouraging results.
Platelet-Rich Plasma for Diabetic Ulcer Healing
Study note: diabetic foot ulcers remain a major clinical problem. Among several strategies, autologous platelet‑rich plasma (PRP) gel has emerged as a promising method to promote healing by concentrating a patient’s own growth factors at the wound site.
Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of clean diabetic foot ulcers, M Ahmed, 2017
What advanced options exist for pressure ulcers and non‑healing wounds?
Pressure ulcers benefit from strategies that reduce pressure, manage moisture, and encourage tissue regrowth. Options include hydrocolloid and advanced moisture‑managing dressings, NPWT, and biologic therapies that together support a healthier wound bed and improved rates of closure for chronic, non‑healing wounds.
What can patients expect during a healing journey with advanced wound care?
Expect a structured, patient‑centered process: a thorough initial assessment, a clear personalized plan that combines appropriate advanced modalities, and regular follow‑up to measure progress and make adjustments.
How is the initial wound assessment and care plan created?
The initial visit evaluates wound size and condition, circulation and infection risk, medical history, medications, mobility, and home factors. Using that information the clinician designs a realistic plan that may include debridement, dressings, regenerative therapies, off‑loading or compression, and a timeline for follow‑up and milestones.
What are common healing timelines and follow‑up steps?
Healing timelines vary by wound type, size, and overall health. Many patients see measurable improvement within weeks, but some complex wounds require longer courses with frequent adjustments. Regular visits — typically weekly or biweekly depending on the plan — let clinicians track progress and intervene early if healing stalls.
How does Healix360 ensure clinically grounded results and patient education?
Healix360
Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists focus on evidence‑based protocols, consistent outcome tracking, and clear patient teaching. Our goal is to combine clinical rigor with practical, home‑based delivery so patients get proven therapies without the friction of repeated clinic travel.
What success measures show treatment effectiveness?
We use measurable outcomes — wound size reduction, time to closure, infection rates, and patient‑reported function — to evaluate effectiveness. By pairing advanced therapies with tailored care plans and ongoing data review, Healix360 aims to improve healing times and patient satisfaction while refining treatment choices.
How does patient education support lasting wound management?
Education is fundamental: we teach patients and caregivers how to care for dressings, recognize early signs of infection, manage nutrition and off‑loading, and follow up appropriately. Empowered patients participate in care decisions and are better positioned to maintain gains and reduce recurrence.
To learn more about mobile regenerative wound care or to schedule an evaluation, you can
contact Healix360
directly.
| Treatment | How it works | Expected result |
|---|---|---|
| Platelet-Rich Plasma | Concentrates a patient’s growth factors to stimulate tissue regeneration | Faster, biologically supported healing |
| Negative Pressure Therapy | Applies vacuum to boost blood flow and granulation tissue | Improved wound contraction and closure |
| Biologic Dressings | Maintain a moist, protective environment and deliver growth signals | Accelerated tissue repair |
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of chronic wounds are most commonly treated with advanced therapies?
Advanced therapies are commonly used for diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, and pressure injuries. These wounds often need specialized, multi‑modal care because of underlying circulation problems, infection risk, or pressure‑related tissue loss.
How can patients prepare for their first appointment with a mobile wound care specialist?
Gather recent medical information (diagnoses, medications, prior wound treatments), note any changes in wound appearance, and list questions or concerns. Make the wound accessible for inspection and have a caregiver present if needed — this helps the clinician complete a thorough assessment and create an effective plan.
What role does nutrition play in the wound healing process?
Nutrition is essential: adequate protein, vitamin C, zinc, and other nutrients support collagen production and immune function. We often review diet and recommend targeted supplementation or referrals to a nutritionist when deficits could slow healing.
Are there any risks associated with advanced wound care treatments?
Advanced wound care is generally safe, but possible risks include allergic reactions to products, infection, or procedure‑related complications such as from debridement. Your clinician will review benefits and risks for each treatment and monitor closely to reduce complications.
How often should patients expect follow‑up appointments during treatment?
Follow‑up frequency depends on wound severity and the treatment plan. Many patients are seen every one to two weeks initially so clinicians can track changes and adjust care. As healing advances, visit intervals may lengthen.
What should patients do if they notice signs of infection in their wounds?
Contact your care team right away if you see increasing redness, swelling, warmth, new or increased pain, foul odor, or discharge. Early assessment and timely treatment are key to preventing complications and preserving progress.
Conclusion
Advanced wound care — combining regenerative therapies, targeted debridement, and mobile delivery — offers meaningful benefits: faster healing, fewer complications, and care that fits patients’ lives. If you or a loved one are managing a chronic wound, exploring advanced mobile wound care through Healix360 may be the next practical step toward recovery.