Advanced Chronic Wound Therapies: Mobile & Regenerative Care Guide
Chronic wounds are often stubborn, painful, and life-altering — and they need more than basic bandaging. This guide walks through the most effective advanced therapies for chronic wounds, with a clear focus on regenerative medicine and mobile wound care services. You’ll learn what makes a wound “chronic,” how regenerative approaches support tissue repair, which therapies lead the field, and how mobile care can make treatment easier for patients. We also outline the typical patient journey with Healix360 and offer practical tips caregivers can use every day.
What Are Chronic Wounds and Why Do They Require Advanced Therapies?
Chronic wounds are wounds that don’t progress through the normal stages of healing — commonly defined as lasting longer than four weeks, with some guidelines using a 12-week benchmark. They need advanced therapies because underlying problems (poor blood flow, infection, metabolic disease) often block the body’s usual repair mechanisms. Conditions like diabetes, venous insufficiency, and prolonged pressure on the skin are frequent causes, and standard wound care alone may not be enough to resolve these complex issues.
Which Types of Chronic Wounds Benefit Most from Advanced Treatments?
Advanced therapies are especially helpful for:
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Common in people with diabetes and at high risk for infection and complications if not treated aggressively.
- Venous Leg Ulcers: Resulting from poor venous return; these wounds often need targeted vascular and local therapies to heal.
- Pressure Ulcers: Also called bedsores—these stem from sustained pressure and require specialized approaches to support tissue recovery and prevent recurrence.
What Challenges Make Chronic Wounds Difficult to Heal?
Several factors can stall healing:
- Infection Risk: Ongoing bacterial burden or biofilm slows tissue repair and increases complications.
- Mobility and Access: Limited mobility or difficulty getting to clinics can delay timely care and dressing changes.
- Underlying Health Issues: Diabetes, poor circulation, malnutrition, and other chronic conditions impair the body’s healing response, making advanced, targeted treatments necessary.
How Does Regenerative Medicine Enhance Healing of Chronic Wounds?
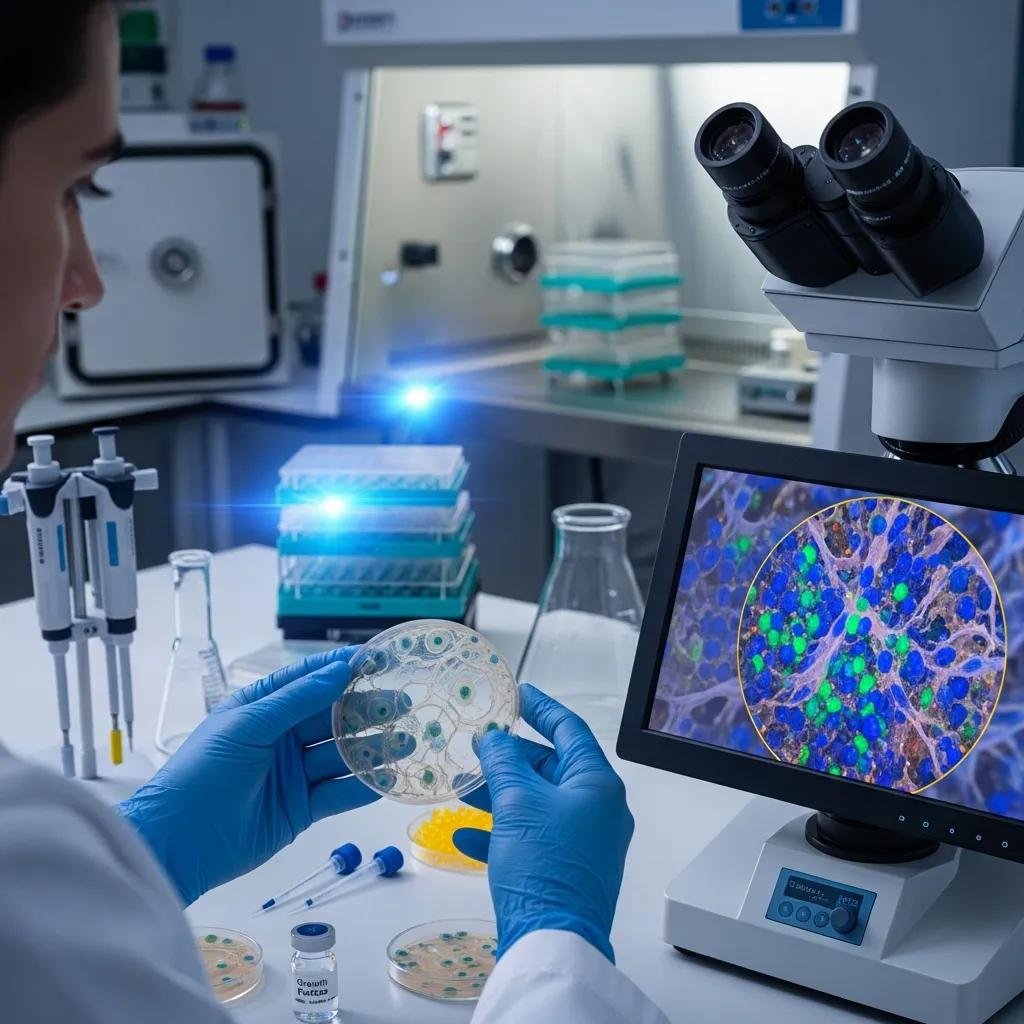

Regenerative medicine helps by activating the body’s repair systems and supplying biological materials that encourage tissue regrowth. Instead of only treating surface symptoms, these approaches aim to rebuild healthy tissue and restore the wound environment so healing can proceed more reliably.
What Is Regenerative Medicine and Its Role in Wound Care?
In wound care, regenerative medicine includes therapies that use cells, growth factors, and extracellular matrix products to guide and speed tissue repair. These biologic tools support cell signaling, reduce inflammation, and provide a scaffold for new tissue — addressing root issues that often keep wounds open.
Which Regenerative Therapies Are Most Effective for Chronic Wounds?
Promising regenerative options include:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Uses stem or progenitor cells to promote repair through trophic and paracrine effects. While some approaches remain investigational, growing evidence supports their role in difficult-to-heal wounds.
- Biologic Dressings: Products that deliver living cells, growth factors, or extracellular matrix components to create a healing-friendly wound bed.
- Growth Factor Therapies: Topical or delivered biologics (for example, PDGF) that stimulate cell migration, proliferation, and new tissue formation.
Recent reviews and trials point to stem cell–based approaches as a promising avenue for promoting cutaneous regeneration in chronic, non-healing wounds.
Stem Cell Therapy and Chronic Wound Regeneration
Summary: Chronic wounds reflect a disrupted wound environment — low oxygenation, tissue damage, and permissive microbial growth — that typical therapies may not fully correct. Stem cell therapies aim to restore repair signals through paracrine and trophic activity, offering a potential route to regenerate skin and support long-term closure. Reviews of current literature call for continued clinical evaluation while highlighting encouraging early results.
Role of stem cell therapies in treating chronic wounds: A systematic review, AC Raghuram, 2020
What Are the Leading Advanced Therapies for Chronic Wounds?
Clinicians use several evidence-backed advanced therapies to tackle chronic wounds. Choice of therapy depends on wound type, size, infection status, and the patient’s overall health.
How Does Debridement Promote Healing in Non-Healing Wounds?
Debridement removes dead or infected tissue to prepare the wound bed for healing. Its benefits include:
- Lowering infection risk: Removing necrotic tissue reduces the bacterial load and biofilm that impede repair.
- Improving blood flow: Clearing nonviable tissue can help local circulation and nutrient delivery.
- Encouraging granulation: A cleaner wound bed supports the growth of healthy granulation tissue needed for closure.
What Are the Benefits of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy at Home?
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) applies controlled suction to the wound and can be used in outpatient or home settings. Key advantages include:
- Faster wound contraction and closure: NPWT often speeds the healing trajectory in complex wounds, including diabetic and pressure ulcers.
- Reduced swelling: Suction helps evacuate fluid and reduce edema, improving tissue perfusion.
- Home-based convenience: Portable NPWT devices allow treatment continuity outside the clinic, which can increase adherence and comfort for patients.
Clinical studies support NPWT as a useful adjunct in preparing complex wounds for closure and improving outcomes in conditions like diabetic foot ulcers.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy in Chronic Wound Management
Overview: Diabetic foot complications remain a leading cause of hospital admission among people with diabetes. Over the last decade clinicians have adopted advanced local therapies, including NPWT, to improve wound bed preparation and healing. Evidence shows NPWT can be especially helpful for complex or hard-to-heal wounds and as a bridge to surgical procedures such as grafts or flaps.
Management of negative pressure wound therapy in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, M Meloni, 2015
Why Choose Mobile Wound Care Solutions for Advanced Chronic Wound Treatment?
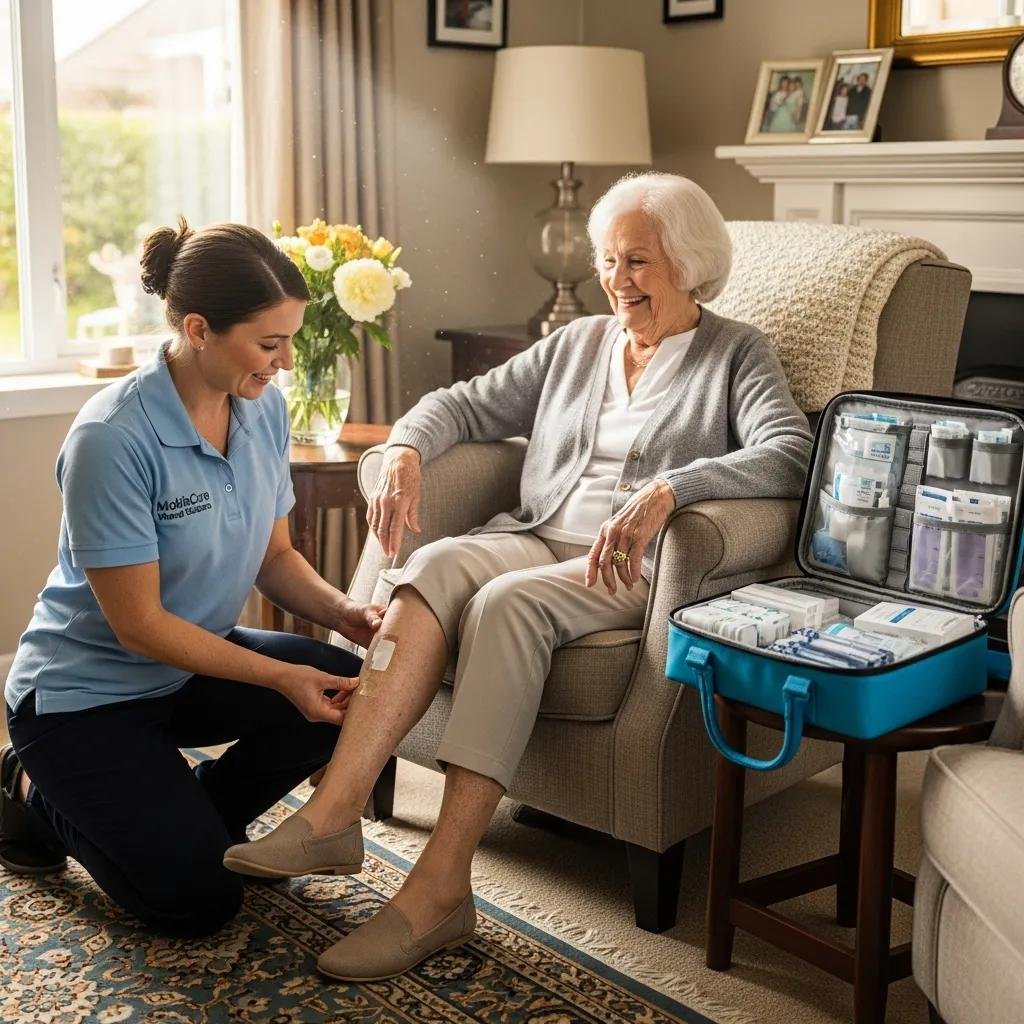

Mobile wound care brings advanced treatments to the patient’s home, reducing travel, improving comfort, and enabling timely interventions. For many patients, this model removes barriers that delay care and helps maintain continuity throughout the healing process.
How Does Mobile Wound Care Improve Patient Convenience and Outcomes?
Mobile teams offer clear benefits:
- Accessibility: Care delivered at home reduces missed appointments and transportation challenges.
- Comfort and dignity: Familiar surroundings can lower anxiety and improve cooperation with treatment.
- Faster response: Mobile clinicians can assess changes quickly and adjust therapy before small problems become complications.
Technology such as secure mobile apps can streamline follow-up and documentation, though access to devices remains uneven across populations.
Mobile Applications for Wound Care Follow-Up
Findings: Early studies show technology-assisted follow-up is feasible and can improve monitoring after emergency or clinic visits. However, disparities in smartphone access and digital literacy can limit reach, so blended models of care remain important.
Wound care follow-up from the emergency department using a mobile application: a pilot study, ML Tolins, 2019
What Personalized Care Does Healix360 Provide in Mobile Settings?
Healix360’s Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists deliver individualized care that includes comprehensive assessments to define wound needs, customized treatment plans matched to the wound type and patient health, and ongoing education and support so patients and caregivers can manage care confidently between visits.
What Is the Patient Journey for Advanced Chronic Wound Therapies with Healix360?
A consistent, patient-focused pathway helps ensure better outcomes. Healix360 structures care so each step builds toward durable healing.
What Are the Steps from Initial Assessment to Full Recovery?
The typical pathway includes:
- Initial Assessment: A full clinical review of the wound, vascular status, infection risk, and overall health.
- Treatment Plan Development: A tailored plan that may combine debridement, biologics, NPWT, offloading, or other modalities.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular visits and remote check-ins to track healing, adjust therapy, and support adherence.
How Are Common Patient Concerns Addressed During Treatment?
We focus on clear communication and comfort: patients receive plain-language education about the wound and treatment, evidence-based pain management strategies, and a direct line for questions so concerns are addressed promptly. For more information or to reach our team, visit Contact Healix360.
How Can Patients and Caregivers Support Healing with Advanced Therapies?
Healing is a team effort. Patients and caregivers who follow key steps often see better results.
What Practical Wound Care Tips Should Caregivers Know?
Simple, consistent practices help:
- Keep the wound clean and protected: Follow dressing and hygiene instructions to reduce infection risk.
- Watch for warning signs: Increased redness, warmth, swelling, foul odor, or new pain warrant prompt clinician contact.
- Follow the care plan: Timely dressing changes, offloading, and medication adherence matter for long-term success.
What Are Realistic Healing Timelines and Pain Management Strategies?
Expect variability: many chronic wounds improve over weeks to months depending on size, depth, infection status, and the patient’s overall health. Pain can be managed with prescribed medications, careful handling during dressing changes, topical therapies when appropriate, and relaxation or breathing techniques to reduce anxiety. Peer support and shared experiences can also help patients stay engaged through longer treatment courses.
| Therapy Type | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Debridement | Removal of dead or infected tissue to prepare the wound bed | Reduces infection risk and encourages new tissue growth |
| Negative Pressure Wound Therapy | Suction-assisted system that manages fluid and promotes tissue contraction | Can speed healing, reduce edema, and improve wound bed preparation |
| Regenerative Medicine | Biologic products (cells, growth factors, ECM) that support tissue repair | Stimulates regeneration and addresses underlying healing deficits |
This table highlights common advanced therapies and their core benefits. Knowing these options can help patients and care teams choose an effective, individualized plan.
Chronic wounds demand coordinated, specialized care that addresses the wound and the person living with it. Regenerative medicine and mobile wound care expand treatment options and remove barriers to care. Healix360’s mobile specialists are committed to personalized plans, clear communication, and measurable progress — so patients regain comfort, function, and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs that a chronic wound is infected?
Look for increased redness, warmth, swelling, new or worsening pain, and discharge that is cloudy, green, or foul-smelling. Fever or spreading redness around the wound are urgent signs. If you notice these changes, contact your care team promptly so infection can be assessed and treated.
How can nutrition impact the healing of chronic wounds?
Nutrition is a foundation of healing. Adequate protein, vitamins (notably A and C), zinc, and overall calories support tissue repair and immune function. Staying well-hydrated also helps skin integrity. A clinician or nutritionist can recommend supplements or meal adjustments when dietary intake is inadequate.
What role does patient education play in chronic wound management?
Education empowers patients to follow care plans, spot complications early, and participate in decisions about treatment. Understanding why a therapy is chosen and how to perform daily care increases adherence and often improves outcomes.
Are there any emerging technologies in chronic wound care?
Yes. Telemedicine enables remote assessments and follow-up, while “smart” dressings and sensor systems can monitor moisture, temperature, or biochemical markers. These technologies can enhance early detection of problems and improve care coordination, though access and cost remain factors to consider.
How can caregivers support patients with chronic wounds?
Caregivers help by keeping the wound clean, following dressing and medication instructions, monitoring for warning signs, and providing emotional support. Encouraging adherence to offloading, nutrition, and follow-up appointments makes a meaningful difference in recovery.
What are the potential complications of untreated chronic wounds?
Without appropriate treatment, chronic wounds can worsen, become infected, or lead to cellulitis, bone infection (osteomyelitis), sepsis, or in extreme cases, amputation. Early, consistent management reduces these risks and improves the chance of lasting closure.
Conclusion
Advanced therapies — from debridement and NPWT to regenerative biologics — expand the tools clinicians use to heal chronic wounds. Mobile care models make these therapies more accessible and keep patients connected to the treatment they need. Healix360 is dedicated to building personalized, evidence-based plans that prioritize comfort, function, and long-term healing. When you’re ready, our team can help you explore advanced wound care options and take the next step toward recovery.