Acute vs Chronic Wound Healing: Key Differences and Treatment Options
Healing a wound is more than bandages and time — it’s a process shaped by the injury, the person’s health, and the care they receive. Acute wounds usually follow a predictable recovery path and heal within weeks. Chronic wounds, however, linger past the normal timeline and often signal underlying health issues that need attention. This guide explains what acute and chronic wounds are, how they heal, common causes and warning signs, and the treatment options available — including how mobile specialty care from
Healix360 Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists
can help patients manage wounds safely and effectively at home.
What Are Acute Wounds and Their Healing Stages?
Acute wounds result from a sudden injury and usually heal in a predictable sequence over days to weeks. Typical causes include cuts, surgical incisions, and burns. The body progresses through defined stages—hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling—each playing a specific role in restoring the skin.
How Do Acute Wounds Heal? Understanding the Normal Healing Process
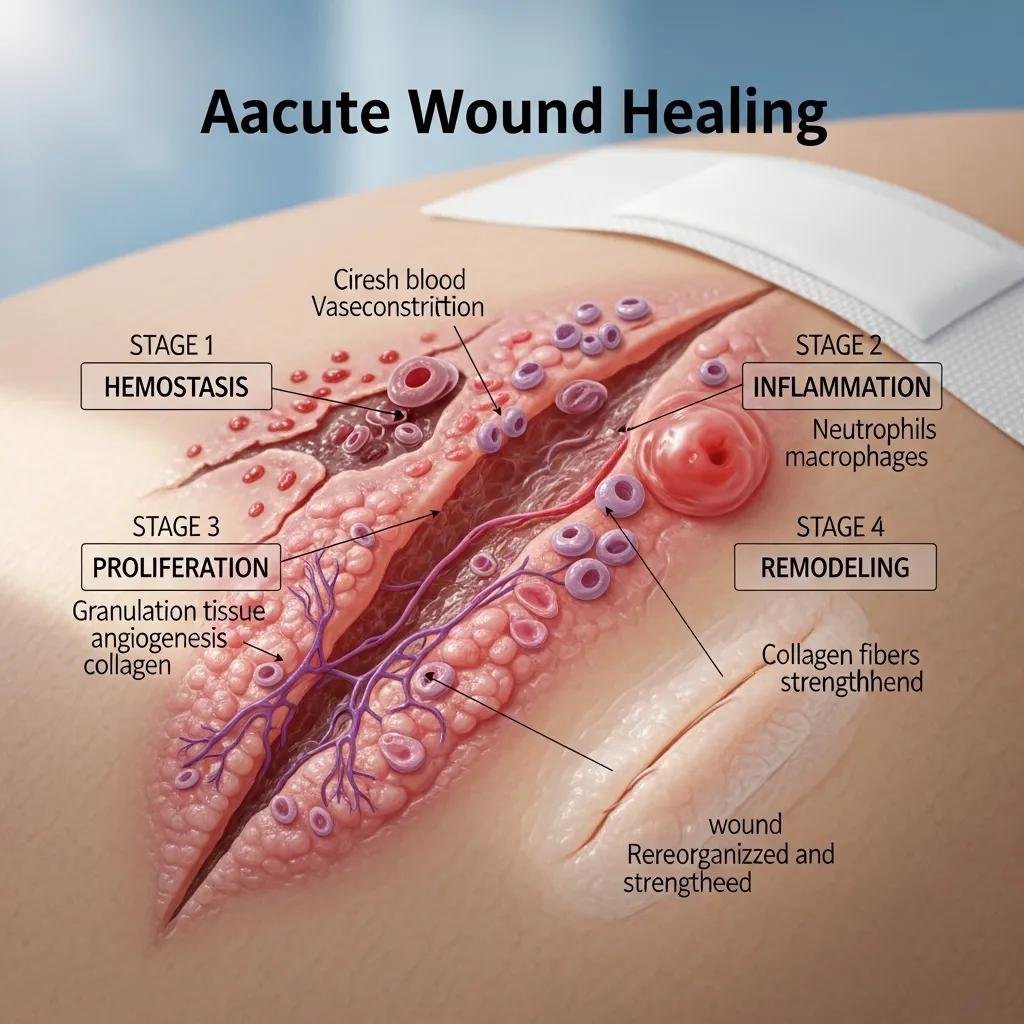
Healing starts with hemostasis, where clotting stops bleeding. Next, inflammation clears debris and defends against infection. During proliferation the body builds new tissue and blood vessels, and remodeling gradually strengthens and reorganizes that tissue. Each stage is essential for restoring skin integrity and function.
What Are Common Causes and Symptoms of Acute Wounds?
Common causes of acute wounds include:
- Trauma
: Cuts, abrasions, and injuries from accidents or falls. - Surgical Wounds
: Controlled incisions made during procedures. - Burns
: Damage from heat, chemicals, or electrical exposure.
Typical symptoms are pain, redness, swelling, and bleeding — signs that usually diminish as the wound moves through the normal healing stages.
What Defines Chronic Wounds and Why Do They Persist?
Chronic wounds are those that fail to heal within an expected period — commonly considered wounds that remain open after three months. They often reflect ongoing problems such as poor circulation, uncontrolled diabetes, or prolonged pressure. Because they don’t follow the usual repair timeline, chronic wounds need targeted evaluation and long-term care.
Clinical research highlights distinct features of chronic wounds and outlines practical management principles clinicians use to improve outcomes.
Chronic Wound Definition, Types & the TIME Treatment Principle
Chronic wounds don’t progress through the normal, timely sequence of repair and are frequently treated incorrectly. Their morbidity and healthcare costs make prevention and guideline-based treatment essential. Common lower-extremity wounds include arterial, diabetic, pressure, and venous ulcers. The TIME framework—tissue debridement, infection control, moisture balance, and edge management—remains central to effective care.
Chronic wounds: evaluation and management, 2020
What Are the Main Causes and Symptoms of Chronic Wounds?
The most common contributors to chronic wounds include:
- Diabetes
: High blood sugar impairs circulation and immune response, slowing repair. - Vascular Disease
: Reduced blood flow limits oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues. - Pressure Ulcers
: Constant pressure causes tissue breakdown over bony areas.
Signs of chronic wounds can include ongoing pain, persistent swelling, slow or stalled healing, and necrotic tissue — all of which complicate recovery and require coordinated care.
Why Do Chronic Wounds Become Non-Healing? Biological and Clinical Challenges
Several factors can halt healing: prolonged inflammation, bacterial biofilms that resist treatment, repeated tissue stress, and unaddressed medical conditions. Successful management not only treats the wound bed but also addresses these biological and clinical drivers behind delayed healing.
The complex biology behind wound repair helps explain why chronic wounds need specialized strategies to restore tissue and prevent recurrence.
Chronic Wound Healing: Process, Causes & Treatments
Wound repair is a tightly coordinated process essential to skin barrier function. Disease states and other factors can disrupt this cascade, producing chronic, non-healing wounds that cause pain and disability while consuming substantial healthcare resources. Even with optimal care, healed wound tissue may not fully match its original strength, and multiple abnormal healing states can lead to persistent wounds.
Chronic wound healing: a review of current management and treatments, 2017
How Do Acute and Chronic Wounds Differ? A Clear Comparison
What Are the Key Differences in Healing Time, Causes, and Treatment?
| Aspect | Acute Wounds | Chronic Wounds |
|---|---|---|
| Healing Time | Generally resolves within weeks | Persists for months or longer; often defined as not healing within three months |
| Common Causes | Trauma, surgery, burns | Diabetes, vascular disease, pressure-related injury |
| Treatment Focus | Prompt wound care and closure | Long-term management, treating underlying conditions, and specialty therapies |
Which Complications Are Unique to Chronic Wounds?
Chronic wounds can lead to serious complications, including:
- Infection
: Ongoing exposure increases the chance of local and systemic infection. - Amputation Risk
: Severe cases—particularly some diabetic foot ulcers—may require surgical removal of tissue or limb. - Reduced Quality of Life
: Persistent pain, limited mobility, and emotional strain affect daily living.
Recognizing and addressing these risks early improves outcomes and reduces long-term impact.
What Advanced Treatment Options Are Available for Chronic and Non-Healing Wounds?
How Does Regenerative Medicine Improve Chronic Wound Healing?
Regenerative approaches—such as cellular therapies, growth factors, and biologic dressings—support tissue repair by targeting underlying biological deficits. These therapies can jump-start stalled healing and are often used alongside standard wound care and optimization of medical conditions.
What Are the Benefits of Mobile Wound Care for Patients with Chronic Wounds?
Mobile wound care, like the services provided by Healix360 Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists, offers practical advantages for patients with chronic wounds:
- In-home Care
: Professional wound assessment and treatment delivered where patients are most comfortable. - Reduced Travel Burden
: Eliminates transportation challenges for patients with limited mobility or chronic conditions. - Personalized Treatment
: Care plans tailored to the person’s overall health, wound characteristics, and recovery goals.
These options make specialist care more accessible and can lead to better, more consistent healing outcomes.
How Can Patients and Caregivers Manage Wound Care Effectively?
What Are Practical Tips for Managing Chronic Wounds at Home?
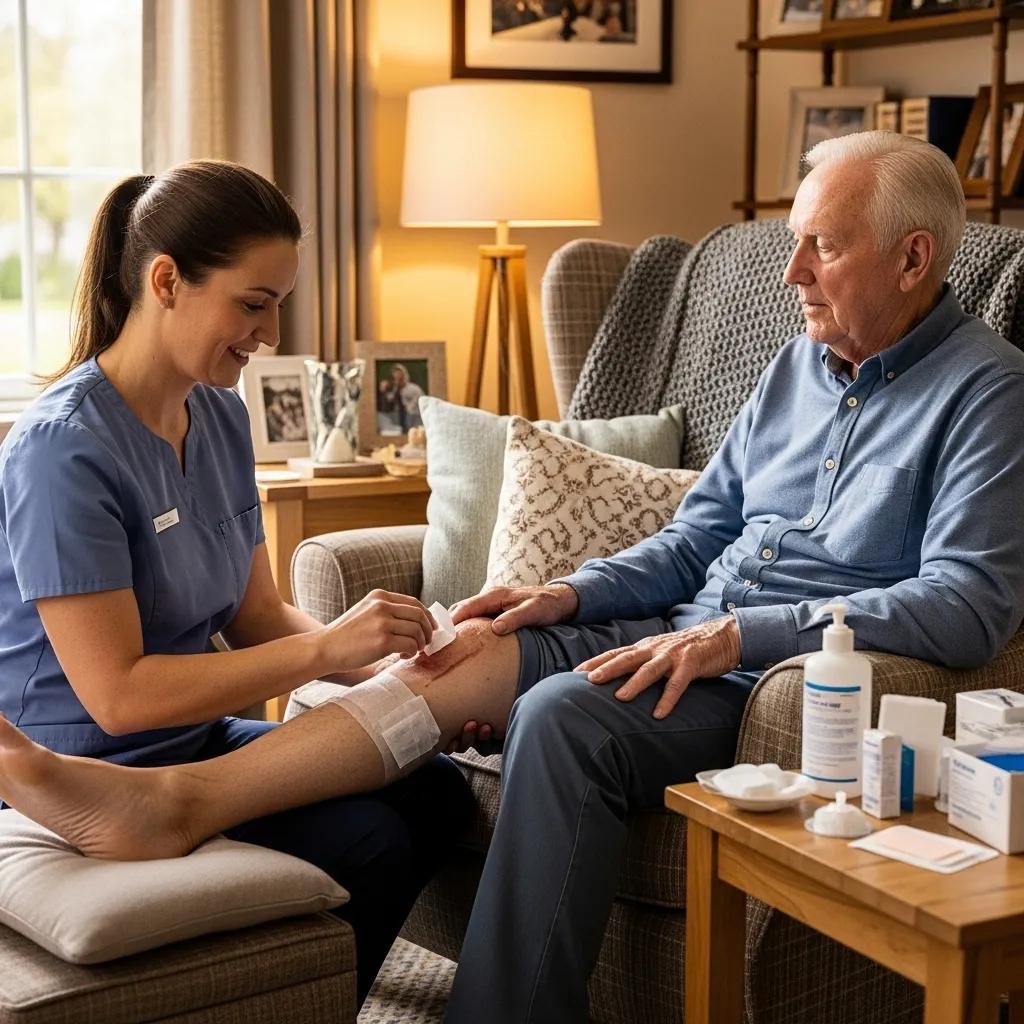

Patients and caregivers can use these practical steps to support wound healing at home:
- Clean the Wound Regularly
: Follow recommended cleaning techniques to minimize infection risk. - Change Dressings as Directed
: Maintain an appropriate moisture balance and protect the wound environment. - Monitor Progress
: Track size, drainage, odor, and pain; report concerning changes promptly.
Consistent care and clear communication with the wound team meaningfully improve recovery chances.
How Does Healix360 Support Patients and Caregivers Through Education and Care?
Healix360 Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists combine hands-on treatment with practical education. We teach wound care techniques, explain warning signs to watch for, and advise when to seek urgent care — all to help patients and caregivers feel confident and supported throughout recovery.
When Should You Seek Professional Care for Acute or Chronic Wounds?
What Signs Indicate the Need for Expert Wound Care?
Contact a clinician if you notice any of the following:
- Worsening Redness or Swelling : The area around the wound becomes increasingly inflamed.
- Foul Odor
: A persistent bad smell can signal infection. - Increasing or Persistent Pain
: Pain that intensifies or fails to improve with usual care.
These signs require prompt evaluation to avoid complications and preserve healing potential.
How to Access Healix360’s Mobile Wound Care Services in Southern California?
To arrange mobile wound care from Healix360, patients can
contact our team directly
. We serve multiple Southern California counties, including Los Angeles, Orange, San Diego, Riverside, San Bernardino, Ventura, and Kern. Scheduling is straightforward so patients receive timely, specialized care when they need it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the long-term effects of untreated chronic wounds?
Left unmanaged, chronic wounds can lead to persistent pain, repeated infections, and in severe cases, tissue loss or amputation. They can also trigger systemic problems like sepsis and cause lasting impacts on mobility, mental health, and quality of life. Early, coordinated care reduces these risks and supports better recovery.
How can nutrition impact wound healing?
Nutrition is a cornerstone of repair. Adequate protein, vitamins (notably A and C), minerals such as zinc, and proper hydration support tissue rebuilding and immune function. Patients with chronic wounds should discuss nutrition with their care team or a dietitian to optimize healing.
What role does infection control play in wound management?
Controlling infection is essential, especially for chronic wounds that are prone to bacterial growth and biofilms. Key measures include gentle cleansing, timely dressing changes, targeted topical or systemic treatments when indicated, and regular monitoring for infection signs. Effective infection control improves outcomes and prevents complications.
Are there specific dressings recommended for chronic wounds?
Several dressings are designed to support chronic wound healing — hydrocolloid, alginate, and foam are common choices depending on exudate levels and tissue condition. Some dressings include antimicrobial features. The optimal dressing is chosen based on the wound’s needs and clinical goals; consult your wound specialist for the best option.
How can caregivers support patients with chronic wounds?
Caregivers make a major difference by helping with daily wound care, ensuring good nutrition and hydration, watching for infection or changes, and providing emotional support. Learning proper techniques from clinicians and keeping consistent communication with the care team helps patients stay on track.
What advancements are being made in chronic wound treatment?
Advances include regenerative therapies (cellular treatments and bioengineered skin substitutes), improved biologic dressings, and technologies that enhance infection control and tissue regeneration. Telemedicine and mobile wound clinics also expand access to specialized care, bringing evidence-based treatments to patients who need them most.
Conclusion
Knowing the differences between acute and chronic wounds helps patients and caregivers take the right actions. Early assessment, targeted treatment, and attention to underlying health issues are key to better outcomes. For many patients, mobile specialty care from Healix360 can remove barriers to treatment and deliver consistent, expert wound management at home. Learn more about our services and take the next step toward healing.