How at‑Home Wound Care Helps Heal Diabetic Ulcers Faster
Bringing wound care into the home is changing how we treat diabetic ulcers. At‑home care delivers specialist treatment where patients are most comfortable, removes common barriers to care, and supports better healing. Below, we explain how mobile wound care improves outcomes, outline advanced therapies used in the field, and highlight the supports available to patients and caregivers. Learn more about our at‑home care model so you can make confident decisions about wound management.
Diabetic foot ulcers are a frequent and serious complication of diabetes. Left untreated, they can lead to infection and other complications. This guide describes what causes these ulcers, why mobile wound care can help, and which advanced treatments can speed recovery. We also cover caregiver support and how mobile services are coordinated.
What Causes Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Why They Require Specialized Care
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores that form on the feet of people with diabetes, most often because of nerve damage (neuropathy) and reduced blood flow. Small injuries — a cut, blister, or pressure point — can become deep, slow‑healing wounds when sensation is reduced and circulation is poor. These wounds often need targeted, specialist treatments to heal and to prevent complications like infection or tissue loss.
What Causes Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Risk Factors?
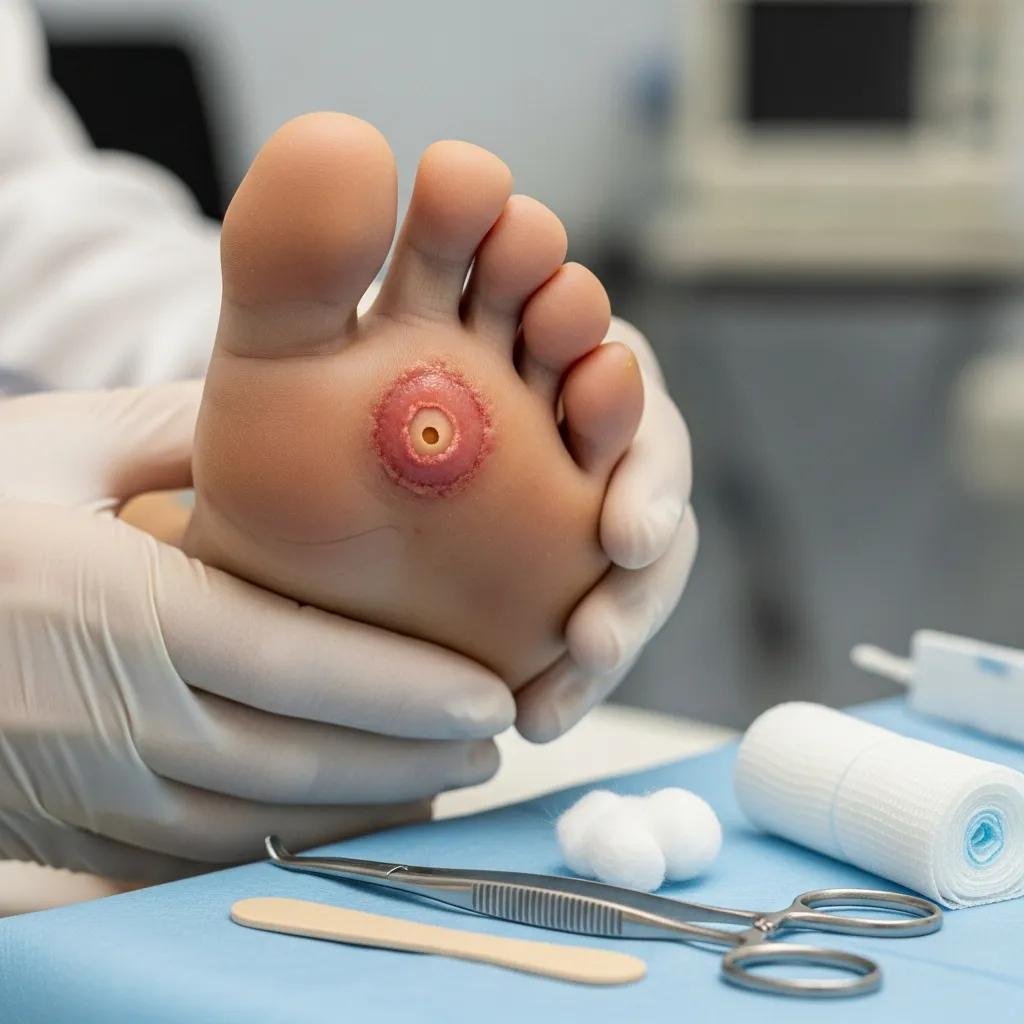
Common contributors to diabetic foot ulcers include:
- Peripheral neuropathy: Nerve damage reduces feeling in the feet, so small injuries often go unnoticed.
- Poor circulation: Diabetes can impair blood flow to the feet, slowing the body’s ability to heal.
- High blood sugar: Elevated glucose impairs immune response and tissue repair, increasing infection risk.
Recognizing these risk factors helps patients and caregivers prevent wounds and act quickly when one develops.
Why Is Traditional Clinic-Based Wound Care Often Insufficient?
Clinic‑based care can miss important needs for many patients:
- Transportation barriers: Travel can be hard or impossible for people with limited mobility or without reliable transport.
- Inconvenience: Repeated clinic visits are disruptive and may be skipped, delaying treatment.
- Missed appointments: Scheduling challenges and health limitations increase the chance of missed visits, which can slow healing.
These realities make a strong case for more accessible, patient‑centered care options.
How Does Mobile Wound Care Provide Advantages for Diabetic Ulcer Treatment?
What Convenience and Accessibility Benefits Does At-Home Care Offer?
At‑home care removes many practical obstacles. Key advantages include:
- No travel required: Care happens where the patient lives, removing the burden of transportation.
- Comfort and calm: Familiar surroundings reduce stress and often improve cooperation with treatment.
- Flexible scheduling: Mobile teams can arrange visits that fit the patient’s day, improving adherence to care plans.
These conveniences help patients stay on track with treatment, which supports better outcomes.
Evidence shows continuous home wound care—when supported by trained caregivers and specialist oversight—can be effective for diabetic foot ulcers.
Continuous Home Wound Care for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
When trained family caregivers work under specialist supervision, home‑based wound care—following debridement and infection control—can continue safely and support healing.
Effectiveness of continuous home wound care on patients with diabetic foot ulcers, 2024
How Does Mobile Care Reduce Infection Risk and Improve Healing Outcomes?
Mobile wound care supports better clinical results by:
- Lower infection risk: Care in a controlled home environment can reduce exposure to pathogens common in outpatient settings.
- Faster healing: Individualized plans and frequent, consistent care help wounds close sooner.
- Tailored treatment adjustments: Regular in‑home assessments let clinicians adapt dressings and therapies as healing progresses.
Together, these factors lead to improved healing and fewer complications.
What Advanced Treatments Are Used in Mobile Diabetic Wound Care?
How Is Debridement Performed in Mobile Settings?
Debridement—removing dead or infected tissue—is a foundational step in wound care. In the home, trained clinicians use several safe techniques:
- Sharp debridement: Using sterile instruments to remove necrotic tissue quickly and precisely.
- Enzymatic debridement: Applying topical agents that help dissolve dead tissue over time.
- Autolytic debridement: Leveraging the body’s own enzymes and moisture under dressings to break down devitalized tissue.
Each method is chosen based on wound type, patient safety, and the overall treatment plan.
What Roles Do Biologic Dressings and Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Play?
Two commonly used advanced tools in mobile wound care are:
- Biologic dressings: These provide a moist healing environment and can deliver growth factors that support tissue repair.
- Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT): A controlled suction system removes excess fluid and stimulates blood flow, promoting granulation and faster closure.
Both approaches are supported by clinical evidence and are adaptable for safe use in the home when supervised by trained clinicians.
| Treatment | How it works | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Biologic Dressings | Maintain moisture and deliver growth factors | Speeds healing, lowers infection risk |
| Negative Pressure Wound Therapy | Removes excess fluid and increases perfusion | Faster granulation, improved wound environment |
| Debridement | Removes dead tissue | Reduces infection risk and prepares the wound to heal |
How Do Regenerative Therapies Accelerate Healing of Diabetic Wounds?
What Are Stem Cell and Growth Factor Therapies in Wound Healing?
Regenerative treatments use biological agents to stimulate repair. Examples include stem cell‑based approaches and therapies that supply growth factors directly to the wound. These methods aim to:
- Boost tissue regeneration: Stem cells can support the formation of new, healthy tissue.
- Increase growth factor support: Supplemental growth factors encourage the cellular processes needed for repair.
Research is ongoing, but these therapies show promise for improving healing in difficult‑to‑treat wounds.
How Do These Therapies Improve Healing Timelines and Outcomes?
Clinical studies suggest regenerative approaches can:
- Shorten healing time: Enhanced cellular activity can lead to faster wound closure.
- Improve outcomes: Patients receiving these therapies may experience better long‑term tissue repair and reduced complication rates.
When appropriate, regenerative therapies can be integrated into a mobile care plan to support recovery.
What Support and Resources Are Available for Patients and Caregivers in Mobile Wound Care?
How Does Healix360 Educate and Support Patients and Caregivers?
Healix360 provides practical education and hands‑on support, including:
- Clear informational materials: Printed and online guides that explain wound care steps and best practices.
- Workshops and caregiver training: Practical sessions to teach safe dressing changes and monitoring techniques.
- Access to specialists: Direct consultations with wound care experts for personalized advice.
These resources are designed to give patients and caregivers the skills and confidence to participate in the healing process.
What Role Does Telehealth Play in Ongoing Mobile Wound Care?
Telehealth is a key part of modern mobile wound care. It offers:
- Remote consultations: Quick access to clinicians without extra travel.
- Ongoing monitoring: Regular virtual check‑ins to track progress and adjust treatment.
- Greater convenience: Patients and families value the flexibility telehealth provides between in‑person visits.
Wider access to the internet and smartphones has made telemedicine a practical, effective tool for managing chronic wounds.
Telemedicine for Chronic Wound Management with Mobile Devices
The rise of internet access and smart devices enables telemedicine to play a meaningful role in chronic wound management, improving access and follow‑up.
Telemedicine in chronic wound management: systematic review and meta-analysis, 2020
Used alongside in‑home visits, telehealth helps maintain continuity of care and ensures timely adjustments to treatment.
Integrated care pathways that combine web‑based wound records with mobile communication illustrate how telehealth supports continuous follow‑up.
Telemedicine & Mobile Phone Support for DFU Care
A web‑based ulcer record paired with mobile phones enables counseling and communication between community nurses and specialist teams, improving follow‑up care.
An integrated wound-care pathway, supported by telemedicine, and competent wound management—
Essential in follow-up care of adults with diabetic foot ulcers, MM Iversen, 2016
How Is Mobile Diabetic Wound Care Covered by Insurance and What Are the Logistics?
What Does Medicare Part B Cover Regarding Mobile Wound Care?
Medicare Part B commonly covers services related to at‑home wound care when ordered by a physician, including:
- Home health services: Skilled nursing and therapy visits for wound management.
- Durable medical equipment: Necessary supplies and devices used in wound care.
Coverage can vary, so patients should check their specific Medicare plan for details.
How Are Scheduling, Follow-Ups, and Costs Managed in Mobile Care?
Mobile wound care teams simplify logistics by offering:
- Flexible scheduling: Appointments arranged to suit the patient’s needs.
- Regular follow‑ups: Ongoing assessments to keep the plan on track.
- Transparent cost information: Clear explanations of fees and insurance coverage to avoid surprises.
This organized approach reduces stress for patients and families while keeping care consistent.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of mobile wound care compared to traditional methods?
Mobile wound care brings specialist treatment to the home, removing travel barriers and making it easier to stick with the plan. Patients often experience greater comfort, more consistent follow‑up, fewer missed visits, and potentially lower infection rates and faster healing thanks to tailored, frequent care.
How can patients prepare for a mobile wound care visit?
Prepare a clean, well‑lit space where the clinician can work. Have a list of medications, recent medical records, and basic wound history ready. If possible, ask a family member or caregiver to be present to help with questions and follow‑up instructions.
What types of professionals provide mobile wound care services?
Mobile wound care teams typically include registered nurses, nurse practitioners, and wound care specialists trained in advanced wound management. Physical therapists may join the team when mobility or off‑loading is part of the care plan. This multidisciplinary approach ensures thorough, coordinated care.
Are there specific technologies used in mobile wound care?
Yes. Telehealth platforms support remote consultations and monitoring, while mobile assessment tools (including digital imaging) help track progress. Therapies such as negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) are also adaptable for home use under clinical supervision.
How does mobile wound care address the emotional needs of patients?
Care at home reduces anxiety by keeping patients in a familiar environment. Clinicians take time to explain care steps, listen to concerns, and include caregivers in training — building trust and empowering patients to take an active role in recovery.
What should patients do if they experience complications during mobile wound care?
If symptoms worsen — increasing pain, swelling, redness, or other signs of infection — contact your care team right away. Most services offer rapid follow‑up visits or telehealth consultations. Prompt reporting helps clinicians intervene quickly and prevent further problems.
Conclusion
Mobile diabetic wound care improves healing by delivering personalized, specialist treatment in the comfort of the patient’s home. This model reduces barriers, lowers infection risk, and supports better adherence through flexible scheduling and continuous follow‑up. If you or a loved one are managing a diabetic wound, discover how our services can support a safer, faster recovery.







