Wound Healing Stages: A clear, practical guide to the process and advanced care
Wound healing is a coordinated biological process made up of distinct stages that restore tissue form and function. This guide walks through those stages, explains what’s happening at each step, and highlights how advanced care can speed recovery and reduce complications. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or clinician, understanding these phases helps you make better decisions and get better results. We also outline how mobile, specialty wound care — like the services provided by Healix360 Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists — can support healing when challenges arise.
What are the four key phases of wound healing?
Healing typically follows four main phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling (maturation). Each phase has a specific role in closing the wound, controlling infection, rebuilding tissue, and restoring strength. Recognizing these phases makes it easier to track progress and spot when a wound needs extra attention.
How does hemostasis start the repair process?
Hemostasis is the immediate response to injury. Blood vessels constrict and platelets form a clot to stop bleeding. Platelets release growth factors that kick off repair and provide a temporary scaffold for incoming cells. This clot also helps block bacteria and sets the stage for the next phase: inflammation.
What happens during the inflammation phase?
Inflammation follows hemostasis and usually lasts a few days (commonly up to 4–6 days). White blood cells arrive to clear bacteria, debris, and damaged tissue. Typical signs — redness, warmth, swelling, and pain — are part of normal healing. Persistent or excessive inflammation, however, can delay recovery and contribute to chronic wounds, so monitoring this phase is important.
How does the proliferation phase support tissue repair?
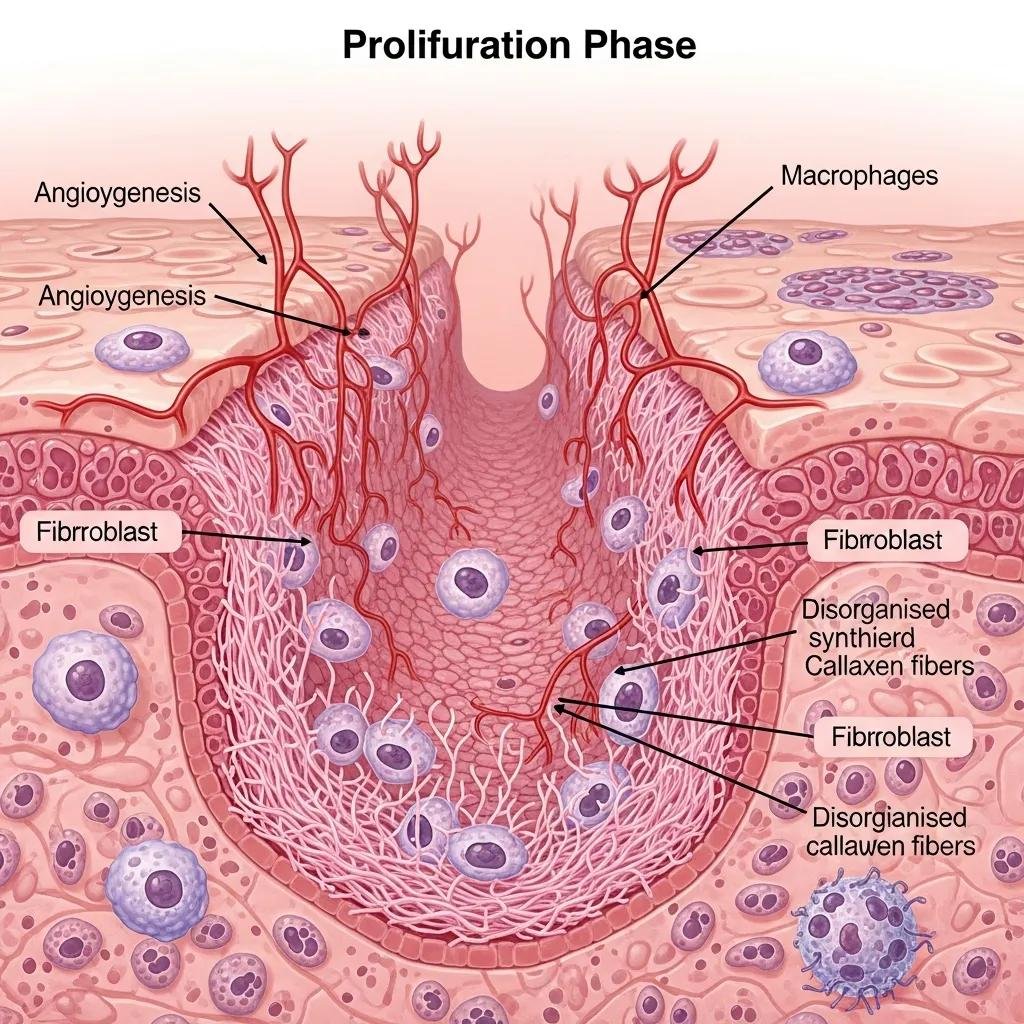
The proliferation phase focuses on rebuilding lost tissue and typically occurs over days to weeks. Key processes include angiogenesis (new blood vessel growth), collagen deposition, epithelialization (skin resurfacing), and formation of granulation tissue that fills the wound bed.
What is granulation tissue and why does it matter?
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue rich in blood vessels and collagen. It indicates the wound is progressing and provides the foundation for cells to migrate and regenerate skin. Healthy granulation is a good sign that the wound is moving toward closure.
How do biologic dressings and growth factors help during proliferation?
Biologic dressings create a moist, protected environment that supports cell migration and tissue growth. Growth factors stimulate specific cell activities needed for repair. Together, these advanced therapies can speed closure and improve outcomes in complex or slow-healing wounds.
What happens during maturation and remodeling?
The remodeling (maturation) phase is the final stage and can last months to years. During this time, collagen is reorganized and strengthened, and the wound gradually gains tensile strength as scar tissue forms and matures.
How is collagen produced and how does scar tissue form?
Fibroblasts synthesize collagen, then the collagen fibers are remodeled and aligned to increase strength and resilience. Although scars rarely restore full original strength, proper remodeling improves function and appearance over time.
Which strategies help manage and monitor scars?
Scar management options include silicone gel sheets, pressure therapy, and regular follow-up to watch for excessive scarring or functional problems. Early, consistent care and monitoring help minimize long-term issues.
What factors influence how quickly and well a wound heals?
Healing depends on many variables: underlying medical conditions, nutrition, mobility, blood flow, and infection control — all influence the timeline and success of recovery.
How do chronic conditions like diabetes affect healing?
Conditions such as diabetes impair circulation and immune responses, which slows healing and raises infection risk. Managing blood sugar, vascular health, and comorbidities is essential for improving outcomes in these patients.
What roles do nutrition, mobility, and infection control play?
Adequate protein and micronutrients support tissue repair. Mobility improves circulation and reduces pressure-related injury. Preventing and promptly treating infection is critical, since infection can halt progress and lead to complications.
How do chronic wounds differ in their healing phases?
Chronic wounds — like diabetic foot ulcers and pressure injuries — often stall and fail to progress through the normal healing sequence. They require targeted assessment to identify and correct the reasons for stalled repair.
Why do some wounds fail to progress?
Failure to heal can come from poor blood supply, ongoing infection, unaddressed pressure or shear, metabolic problems, or other underlying conditions. Identifying these barriers is the first step to getting the wound back on track.
How can regenerative medicine speed healing of chronic wounds?
Regenerative approaches — including advanced biologic dressings, cell therapies, and engineered matrices — aim to restore the wound environment and stimulate the body’s repair mechanisms. When used appropriately, these therapies can accelerate closure and reduce complications in difficult-to-heal wounds.
Recent research highlights a broad and evolving set of regenerative therapies designed to improve chronic wound outcomes and reduce costly complications.
Advanced Treatments & Regenerative Medicine for Chronic Wounds
Chronic wounds pose a global, costly challenge and need more effective treatment options to prevent infection and limb loss. Advances in regenerative medicine offer promising new tools — from customizable polymer matrices to cellular therapies, targeted growth factors, and genetic techniques — that aim to restore tissue function and speed healing in difficult cases.
Current advances in wound healing and regenerative medicine, M Moradi, 2024
What are the benefits of advanced mobile wound care?

Advanced mobile wound care, like the services offered by Healix360 Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists, brings specialty treatment to the patient’s home — improving access, comfort, and continuity of care for people who have trouble reaching clinic-based services.
How does in-home care improve consistency and comfort?
In-home care lets clinicians deliver tailored treatment plans and maintain regular follow-up in the patient’s environment. That consistency improves adherence, reduces travel burden, and often leads to better clinical and patient-reported outcomes.
What role do caregivers play in the healing process?
Caregivers help with daily wound care tasks, observe changes, encourage treatment adherence, and provide emotional support. Their collaboration with clinicians is vital to catch problems early and keep the plan on track.
| Phase | Key Characteristics | Duration | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemostasis | Clot formation, initial response | Minutes to hours | Prevents blood loss, initiates healing |
| Inflammation | Immune response, debris clearance | Days (up to 4-6) | Protects against infection, prepares healing |
| Proliferation | Tissue formation, granulation | Days to weeks | Restores tissue integrity, supports regeneration |
| Remodeling | Collagen remodeling, scar formation | Months to years | Strengthens tissue, improves function |
The table above summarizes each phase’s role and timeline so you can track progress and know when to seek extra support.
Healing is influenced by wound type, patient health, and the care delivered. Understanding the stages and how specialized services like advanced mobile wound care fit into a plan can meaningfully improve outcomes and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs a wound is healing as expected?
Typical signs include gradual reduction in redness and swelling, formation of healthy granulation tissue, less pain over time, and steady wound edge contraction. Color changes from bright red toward a pink, healthier appearance are common. Sudden worsening or new pain, increasing drainage, or foul odor warrant prompt evaluation.
How can I reduce the risk of infection in a healing wound?
Keep the wound clean and covered with appropriate dressings, wash hands before contact, and follow your clinician’s dressing-change schedule. Avoid soaking the wound and protect it from environmental contamination. If you notice increasing redness, swelling, heat, pus, or fever, contact your care team right away.
Which lifestyle changes support faster healing?
Eat a balanced diet with enough protein, vitamins, and minerals; stay hydrated; quit smoking; limit excessive alcohol; and stay as active as your condition allows to support circulation. Managing chronic diseases and reducing stress also help the body repair more effectively.
When should I seek professional medical attention?
Seek care if a wound shows signs of infection (increasing redness, warmth, swelling, pus), if it stops improving after several days, or if you develop fever or unusual pain. Also seek help for deep wounds, animal bites, or wounds contaminated with dirt or foreign material—early treatment prevents complications.
How do advanced wound care products help healing?
Advanced products — hydrocolloids, alginates, biologic dressings, and products with growth factors or antimicrobials — maintain a moist healing environment, manage exudate, and protect the wound. The right product for the wound type improves cell migration and tissue repair while reducing infection risk and pain.
Does emotional health affect wound healing?
Yes. Stress and anxiety can increase inflammation and weaken immune responses, slowing healing. Emotional support, stress reduction, and access to mental health resources can improve recovery. Addressing both physical and emotional needs is part of comprehensive wound care.
Conclusion
Knowing the stages of wound healing helps you recognize normal progress and when to escalate care. Each phase plays a specific role, and timely, targeted intervention improves outcomes. When wounds are complex or healing stalls, specialized options — including advanced mobile wound care from Healix360 — offer tailored support that can speed recovery and improve quality of life. Contact us to learn how our team can help on your healing journey.