Advanced Wound Care for Older Adults: Mobile Treatment & Chronic Wound Solutions
Caring for wounds in older adults requires focused expertise. As we age, the body’s ability to repair itself changes, and chronic conditions can make healing slower and more complicated. This article explains those challenges and outlines modern mobile treatment options that bring effective care directly to the home. You’ll learn about the most common chronic wounds in seniors, the benefits of home-based wound services, and promising regenerative therapies that support recovery. Whether you’re a caregiver or a clinician, this guide shows how Healix360’s Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists can assist at every step of the healing journey — and how to reach us when you’re ready to get started (Contact Healix360).
Why Do Older Adults Heal More Slowly from Wounds?
Older adults often heal more slowly because of normal aging plus long-term health issues. Skin thins and loses elasticity over time, circulation can decline, and immune responses may be blunted — all of which slow the normal repair process. Recognizing these factors helps caregivers and clinicians design safer, more effective wound care plans.
Which Age-Related Changes Slow Wound Repair?
Several age-related changes make wounds harder to heal. Thinner, less flexible skin tears more easily and takes longer to close. Reduced blood flow limits delivery of oxygen and nutrients to injured tissue. And shifts in immune function increase infection risk and can delay repair. Good wound care accounts for each of these factors.
How Do Chronic Diseases Affect Healing in Seniors?
Long-term conditions commonly seen in older adults—especially diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and malnutrition—directly interfere with wound healing. Diabetes can cause neuropathy and poor circulation, reducing sensation and blood supply to the feet and legs. Peripheral vascular disease restricts blood flow to tissues, and inadequate nutrition deprives the body of the proteins and micronutrients it needs to rebuild tissue. Treating these underlying issues is essential to improve healing outcomes.
Which Chronic Wounds Are Most Common in Older Adults?
Chronic wounds are a major concern for seniors and their caregivers. Pressure injuries, diabetic foot ulcers, and lower extremity ulcers are among the most frequent. Knowing how these wounds develop and how they’re treated is key to preventing complications and supporting recovery.
Chronic wounds are often driven by underlying health issues and can have a deep impact on daily life and independence.
Chronic Wounds in Elderly: Causes, Impact, and Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Many wounds remain slow to heal despite standard medical and nursing care. They can stem from complications of chronic disease (for example, diabetes), surgery, prolonged pressure, trauma, or burns. Chronic wounds occur more frequently in older adults and in people with immune or chronic health problems. Left unchecked, they may reduce quality of life, impair function, lead to amputation, or even cause death.
Negative pressure wound therapy: an evidence-based analysis, 2006
How Are Pressure Ulcers Recognized and Treated in Seniors?
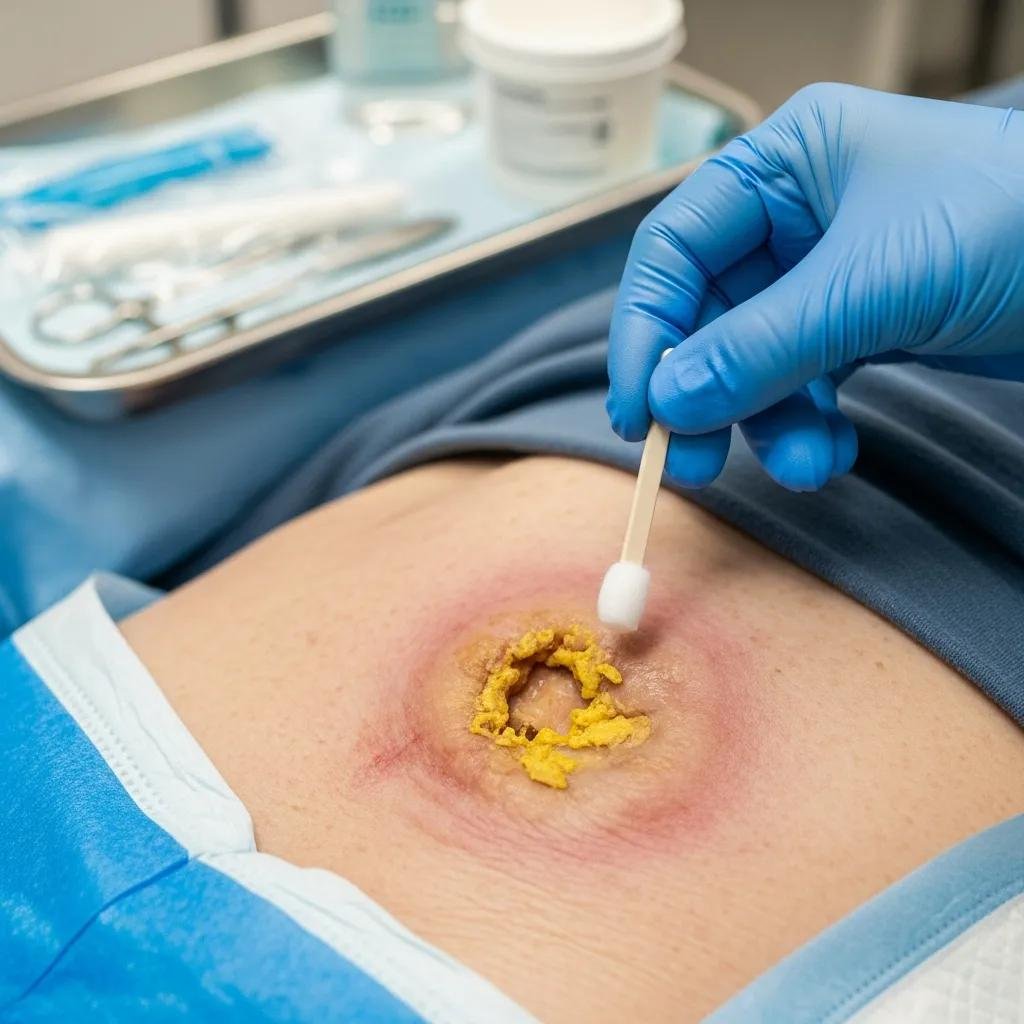
Pressure ulcers (bedsores) typically appear over bony areas in people with limited mobility. Early signs include persistent redness, skin that won’t blanch, or localized warmth. Treatment focuses on relieving pressure, keeping the wound clean, and using appropriate dressings to support a moist healing environment. Prevention—regular repositioning, skincare, and pressure-relieving surfaces—is often the most effective strategy.
What Should You Know About Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Older Patients?
Diabetic foot ulcers are a major risk in older adults with diabetes. Nerve damage (neuropathy), poor circulation, and foot deformities increase the chance of an ulcer forming and reduce its ability to heal. Early detection, offloading pressure from the wound, optimized glycemic control, and advanced dressings or therapies are critical to preventing infection and avoiding serious complications.
How Does Mobile Wound Care Help Older Adults?
Mobile wound care brings skilled clinicians and proven treatments to the home—reducing travel burdens and improving access to timely care. For older adults with mobility or transportation challenges, home visits mean wounds are assessed and treated promptly, which supports better outcomes and greater comfort.
What Convenience and Access Benefits Does Home-Based Care Offer?
Receiving wound care at home removes a major barrier for many older adults: getting to the clinic. Home visits reduce stress, minimize exposure to other illnesses, and let clinicians evaluate the real-life environment where care and prevention happen. Faster access to specialists also means problems are caught earlier and treatment plans can be adjusted without delay.
Accessible, home-based wound care is a recognized and effective approach for older and homebound patients, covering prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Essential Home-Based Wound Care for Elderly and Homebound Patients
Wounds are common in homebound adults; clinicians who care for them need a practical understanding of prevention, diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic options to reduce morbidity and improve comfort. Pressure wounds are among the most frequent issues; lower-extremity ulcers (venous, arterial, or neuropathic) are also common. Home-based providers should be familiar with dressing selection and with home-appropriate therapies such as negative-pressure wound therapy.
Wound care in home-based settings, FC Ko, 2015
How Does Healix360 Tailor Treatment Plans for Older Adults?
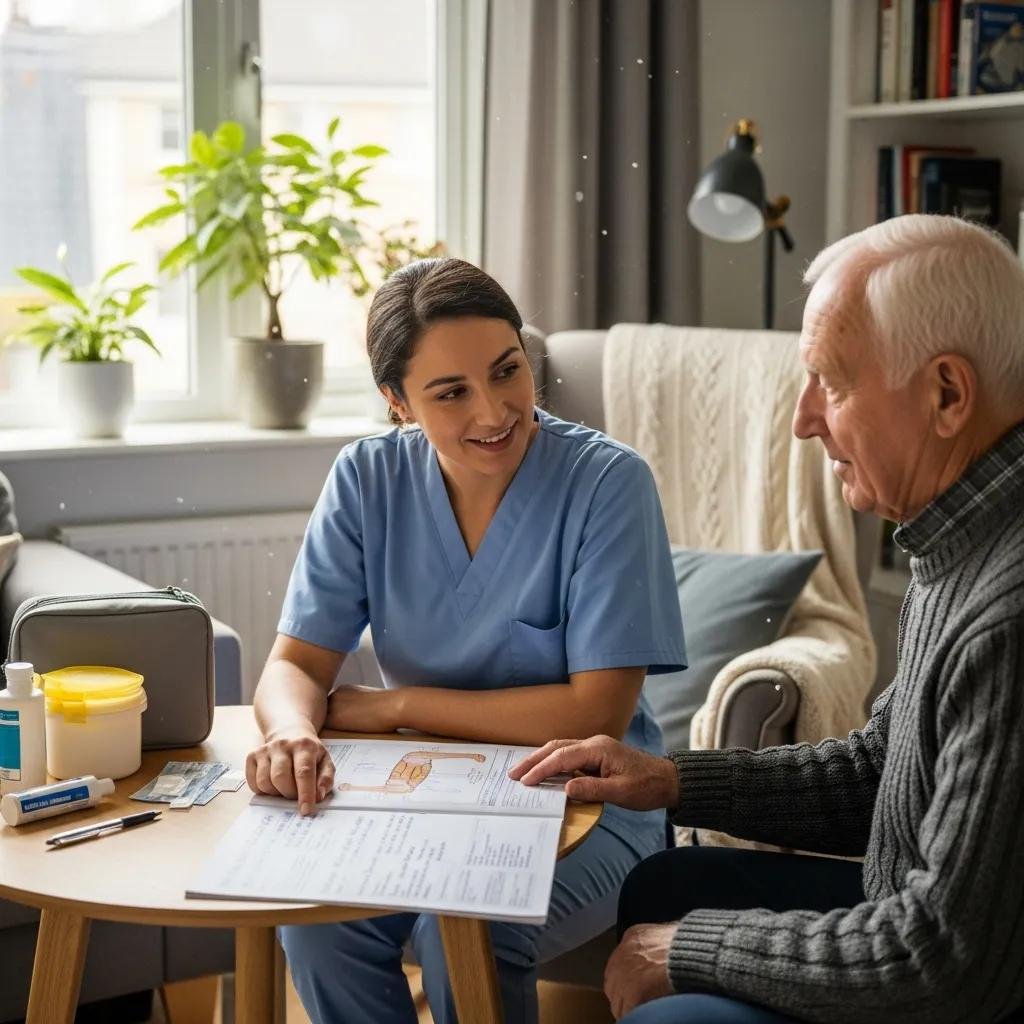

Healix360 — Advanced Mobile Wound Care Specialists create personalized plans based on a thorough assessment of each patient’s wound, medical history, mobility, and care goals. We prioritize treatments that fit the patient’s life—selecting dressings, therapies, and follow-up schedules that support healing while minimizing disruption. Regular monitoring and timely adjustments keep the plan aligned with progress and patient needs.
Which Advanced Regenerative Therapies Support Healing in Older Adults?
Regenerative therapies are expanding the options for chronic wound care. These treatments aim to stimulate tissue repair and reduce inflammation, offering additional tools when standard care alone is insufficient.
How Do Stem Cell and Biologic Therapies Help Wounds Heal Faster?
Stem cell and biologic therapies can accelerate healing by encouraging tissue regeneration and improving the local healing environment. Stem cells may support the formation of new tissue, while biologic dressings supply growth factors and other bioactive ingredients that boost cellular activity and reduce chronic inflammation. These therapies are used selectively, alongside established wound care practices.
Current research highlights the potential role of advanced therapies—like mesenchymal stem cells—in managing complex chronic wounds, particularly in vulnerable patients.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Advanced Therapy for Chronic Wounds in Older Adults
Mesenchymal stem cell–based approaches are especially relevant for treating chronic wounds in older adults, people with diabetes, and patients with autoimmune conditions or compromised endogenous MSCs. These therapies aim to restore healing capacity in challenging clinical situations.
Mesenchymal stem cells in chronic wounds: the spectrum from basic to advanced therapy, M Otero-Viñas, 2016
Why Are Debridement and Negative Pressure Therapy Important?
Debridement removes nonviable tissue that hinders healing and reduces infection risk—it’s a cornerstone of advanced wound management. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses controlled suction to remove excess fluid, reduce edema, and encourage blood flow and granulation tissue. Together, these techniques help manage complex wounds and create conditions that support recovery.
How Can Caregivers Help Support Wound Healing?
Caregivers are central to successful wound recovery. Consistent daily care, good communication with the clinical team, and attention to nutrition and hygiene all improve healing and reduce complications.
Which Nutrition Steps Promote Better Healing in Older Adults?
Nutrition directly affects tissue repair. Ensure older adults receive adequate protein and calories, plus key micronutrients like vitamin C, zinc, and vitamin A when appropriate. Hydration matters, too—fluids support circulation and cellular function. If dietary intake is limited, discuss supplements or nutrition interventions with the care team.
How Should Caregivers Spot and Respond to Infection Signs?
Caregivers should watch for increasing redness, swelling, warmth, worsening pain, new or increased drainage, or a foul odor—these can signal infection. Promptly notify the wound care team if any of these signs appear. Good hand hygiene, clean dressing technique, and following the clinician’s instructions help prevent infections.
What Can Patients Expect When Working with Healix360?
Healix360 provides a coordinated, patient-focused experience. From the first visit through follow-up, our goal is clear communication, consistent care, and measurable progress toward healing.
What Happens at the Initial Assessment?
At the first visit, our clinicians document the wound’s size, appearance, and surrounding skin condition and review the patient’s medical history, medications, and nutrition. We identify factors that may delay healing and set clear, realistic goals for treatment. This assessment forms the basis of a personalized plan shared with the patient and caregivers.
How Do You Track Progress and Manage Pain During Treatment?
We monitor wounds regularly, adjusting dressings and therapies as the wound changes. Pain management is individualized and may include topical or oral medications, repositioning, and non-drug measures such as gentle mobilization or relaxation techniques. The care team keeps patients and families informed about progress and next steps.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs that a wound is healing properly in elderly patients?
Signs of healthy healing include gradual reduction in wound size, formation of new pink/red tissue (granulation), less drainage, and decreasing pain. The absence of spreading redness, increasing warmth, or foul-smelling discharge is also reassuring. If healing stalls or infection signs appear, contact your wound care provider promptly.
How can family members assist in the wound care process for elderly patients?
Family caregivers help most by following dressing-change instructions, watching for infection or changes in the wound, supporting nutrition and hydration, and keeping scheduled appointments. Emotional support and clear communication with the care team also improve adherence and outcomes.
What types of dressings are most effective for elderly patients with chronic wounds?
Appropriate dressing choice depends on the wound’s type, location, and amount of drainage. Common options include hydrocolloid dressings for a moist healing environment, foam dressings for moderate exudate, and alginate dressings for high-exuding wounds. Your clinician will choose dressings that balance protection, absorption, and comfort.
How often should wounds be assessed and dressed in elderly patients?
Assessment and dressing frequency vary with the wound and treatment. Many wounds need at least weekly clinical review; some require daily or every-other-day attention if drainage or infection risk is high. Dressings can range from 1–3 day changes to longer intervals when appropriate—your wound care specialist will advise the schedule.
What role does pain management play in the healing process for elderly patients?
Pain control supports healing by allowing patients to participate in mobility and care while reducing stress-related delays in recovery. Effective pain strategies combine appropriate medications with non-pharmacologic measures such as positioning, wound care techniques that minimize discomfort, and gentle movement as tolerated.
What are the potential complications of untreated chronic wounds in elderly patients?
Without timely care, chronic wounds can become infected, lead to cellulitis, or progress to systemic infection (sepsis). They also cause prolonged pain, loss of mobility, and reduced quality of life; in severe cases, they may require amputation. Early, consistent wound management reduces these risks.
Conclusion
Thoughtful, timely wound care makes a measurable difference for older adults. By recognizing age-related challenges, using home-based services when appropriate, and applying advanced therapies and personalized plans, caregivers and clinicians can improve healing and preserve independence. If you’d like to learn how Healix360 can support your loved one’s recovery, explore our services or reach out to our team today.